- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Exposure to heavy metals may increase osteoporosis risk
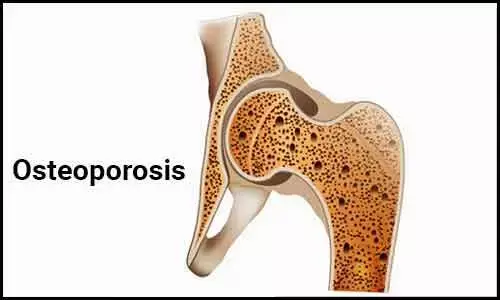
Iran: Exposure to heavy metals such as cadmium and lead may increase the risk of osteoporosis, according to a recent study published in the journal Osteoporosis International.
The relationship between heavy metal exposure and osteoporosis or osteopenia risk has biological plausibility, yet the association remains inconclusive. Therefore, C. Jalili, University of Medical Sciences, Kermanshah, Iran, and colleagues conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the associations between exposure to heavy metals (i.e., cadmium, lead, and mercury) and the risk of osteopenia or osteoporosis.
The researchers searched databases of MEDLINE, Embase, Scopus, and Web of Science through 2019, to identify studies that evaluated the relationship between exposure to cadmium, lead and mercury and risk of osteopenia or osteoporosis in adults. Fourteen eligible studies were included. Effect sizes expressed as pooled odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were estimated using weighted random-effect models.
Read Also: Osteoporosis medicines may lower pneumonia risk, finds study
Key findings of the study include:
- Exposure to cadmium (OR = 1.35) and lead (OR = 1.15) was associated with an increased risk of osteopenia or osteoporosis, unlike mercury.
- Subgroup analyses showed cadmium exposure increased the risk of osteopenia or osteoporosis in older (> 65 yrs.; OR = 1.43) compared with younger (18-65 yrs.; OR = 1.24) adults.
- Lead exposure increased the risk in men (OR = 1.55) unlike in women.
- By contrast to urinary levels, blood (OR = 1.26) and dietary (OR = 1.46) levels of cadmium were associated with an increased risk of osteopenia or osteoporosis.
"Exposure to cadmium and lead may be associated with an increased risk of osteopenia or osteoporosis, although high heterogeneity was detected," concluded the authors.
Read Also: Osteoporosis management during Covid 19 pandemic: Joint multisociety guidance
The study, "Exposure to heavy metals and the risk of osteopenia or osteoporosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis," is published in the journal Osteoporosis International.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


