- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Handheld Navigation Improves Accuracy in Direct Anterior Total Hip Replacement
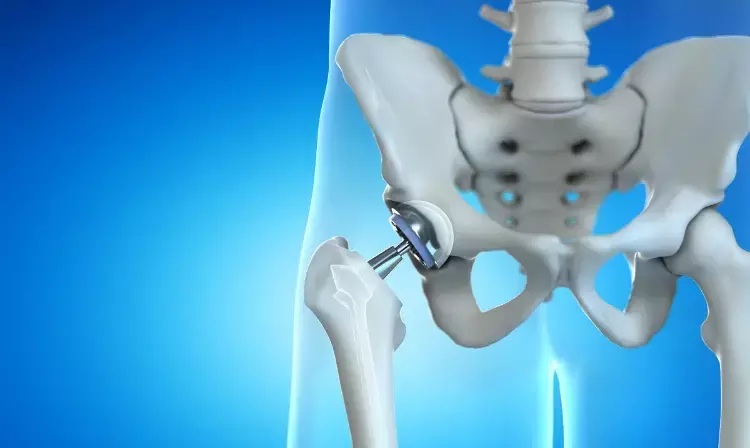
N L Kolodychuk et al conducted a study to determine the accuracy in placing the acetabular component, estimation of leg length, offset, radiation time and dose, and operative time using a handheld navigation device compared to conventional anterior total hip arthroplasty (THA). It also examined the learning curve of the handheld navigation device.
The study has been published in ‘Arthroplasty today’.
Data were prospectively collected for a consecutive series of 159 THAs; 99 THAs with handheld navigation and 60 conventional THAs. Thresholds of <50, >= 50 to <100, and >=100 for acetabular inclination and version and thresholds of <5mm, >=5mm to <10mm, and >=10mm for leg-length and combined offset discrepancy were used to assess accuracy. Fluoroscopy time and exposure, operative time, and complications were compared. Learning curve was determined using operative time. Statistical analysis was performed for the different accuracy thresholds with P values set a <0.05 for significance.
Key findings of the study were:
• The handheld navigation device demonstrated a mean accuracy of 3.20 and 1.80 for version and inclination, respectively.
• The handheld navigation group had significantly fewer outliers in version (P<.001), inclination (P<.001), and offset discrepancy (P<.001).
• Fluoroscopic dose and time (P < .001) were lower in the handheld navigation cohort.
• The learning curve for handheld navigation was 31-35 cases• The mean operative time after the learning curve was similar to that in the conventional fluoroscopy group (P = .113).
The authors concluded that – “this study established that the handheld navigation system provides accurate intraoperative information during DAA THA regarding LLD, combined offset, and acetabular cup position. The use of the handheld navigation system was more accurate and resulted in fewer outliers in LLD, combined offset, and acetabular cup position than conventional fluoroscopy-aided DAA THA, while mitigating radiation time and dose. The learning curve for this handheld navigation system was 31-35 cases. After completion of the learning curve, the use of the handheld navigation system offered extremely accurate cup placement and recreation of leg length and offset, decreased operative time, and significantly fewer outliers in implant position.”
Further reading:
Handheld Navigation Improves Accuracy in Direct Anterior Total Hip Replacement
Nicholas L. Kolodychuk, Jesse A. Raszewski et al
Arthroplasty Today 17 (2022) 58-65
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artd.2022.06.016
MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS
Dr Supreeth D R (MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS) is a practicing orthopedician with interest in medical research and publishing articles. He completed MBBS from mysore medical college, dip ortho from Trivandrum medical college and sec. DNB from Manipal Hospital, Bengaluru. He has expirence of 7years in the field of orthopedics. He has presented scientific papers & posters in various state, national and international conferences. His interest in writing articles lead the way to join medical dialogues. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


