- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Interpretive models could help predict risk of preoperative DVT in elderly patients with hip fracture: Study
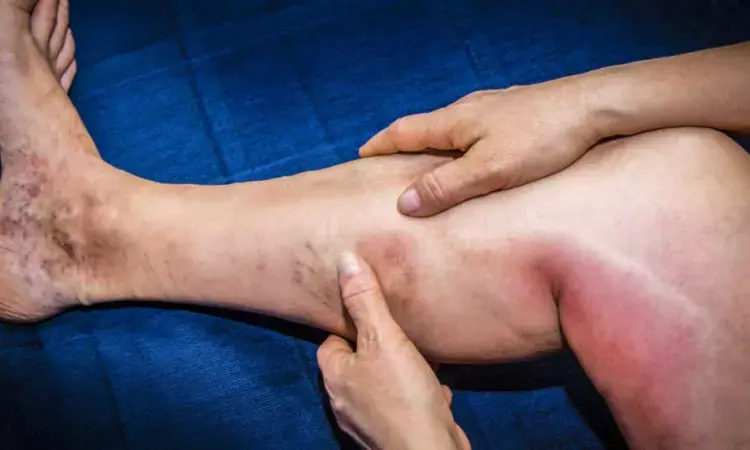
A new study published in the International Journal of General Medicine showed that physicians may reliably estimate the preoperative risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in senior hip fracture patients with the use of interpretable prediction models.
One of the most common fractures among the elderly is a hip fracture. The occurrence of hip fractures among the elderly has been steadily rising as the world's population ages at an accelerated rate, creating a significant worldwide public health problem. Older hip fracture patients often develop deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in their lower limbs. In order to forecast preoperative DVT risk in these patients, this study will create an interpretable machine-learning model. The model will be explained and important parameters will be identified using the SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) approach.
There were 976 patients in all (38 factors) for this study. A training set (N = 683) and a validation set (N = 293) were randomly selected from the dataset. The training set was balanced using the Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE). Key variables were identified using Venn analysis, and influential elements were chosen using Logistic Regression (LR), Random Forest (RF), and Adaptive Boosting (AdaBoost). A prediction model was created using 5 machine learning approaches, including Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost). The SHAP approach was employed for interpretation after the performance of several models was assessed to choose the best algorithm.
Eight variables in all were chosen to be the predictive model's inputs. With an Area Under the Curve (AUC), sensitivity, accuracy, specificity, negative predictive value, positive predictive value, and F1 score of 0.975, 0.923, 0.936, 0.910, 0.909, 0.939, and 0.922, respectively, the XGBoost model performed the best on the training set data.
Also, the decision curve showed that the XGBoost model had a greater net benefit than other machine learning models, and the calibration curve showed a high degree of agreement between the projected probabilities and the actual hazards. The SHAP tool also made it easier to analyze individual forecasts as well as characteristics.
Overall, the current study effectively created an interpretable XGBoost prediction model that showed exceptional performance in predicting preoperative DVT in elderly hip fracture patients. Additionally, individuals who are at high risk for DVT might be properly diagnosed by using a machine learning model that is simple to comprehend and understand. This would enable the prompt and exact administration of relevant therapies.
Reference:
Cheng, Q., Liu, Y., Zhu, P., Cai, W., & Shi, L. (2025). Predicting preoperative deep vein thrombosis in elderly hip fracture patients using an interpretable machine learning model. International Journal of General Medicine, 18, 7271–7282. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJGM.S551225
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


