- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Intra-articular lidocaine reduces pain in anterior shoulder dislocations: Study
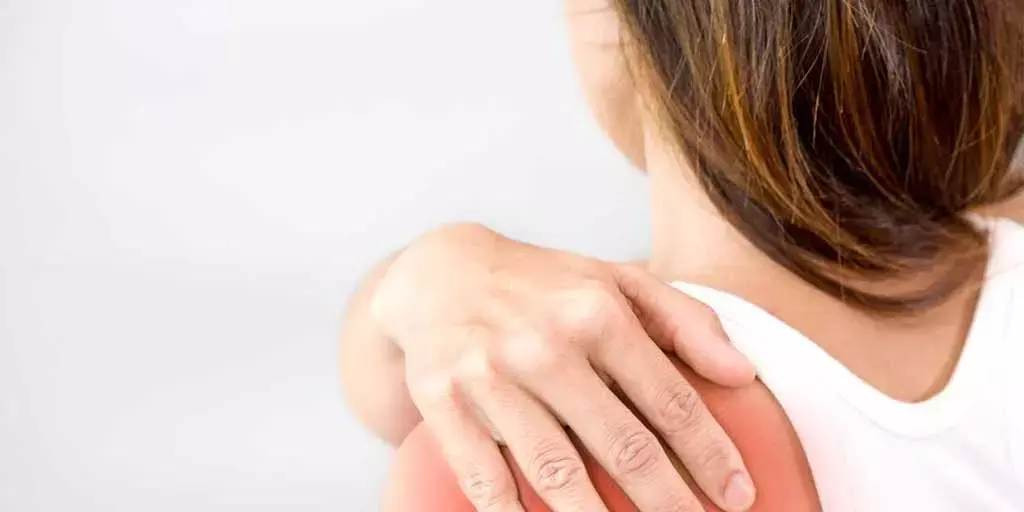
The successful reduction of anterior shoulder dislocations in the emergency department (ED) may be achieved using intra-articular lidocaine in a manner comparable to that of intravenous sedation, says an article published in Canadian Journal of Emergency Medicine.
In the emergency room, anterior shoulder dislocations are often treated. Intra-articular lidocaine (IAL) injection or intravenous sedation are two methods of providing analgesia for reduction (IV sedation). This study was done by Arjun Sithamparapillai and his colleagues to compare closed reduction of acute anterior shoulder dislocation under IAL and IV sedation in the emergency department.
Reference lists were manually searched, and electronic searches of MEDLINE and EMBASE (1946–September 2021) were performed. IAL and IV sedation were compared in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to reduce acute anterior shoulder dislocations in ED patients under the age of 15. A successful reduction, adverse events, duration of stay in the emergency department, pain ratings, ease of reduction, procedure time, patient satisfaction, and cost were among the outcomes of interest. Two reviewers independently selected abstracts, judged the caliber of the studies, and collected data. Mean differences and risk ratios (RR) with 95% confidence intervals were produced as a result of pooling the data using random-effects models.
The key findings of this study were:
1. A total of 630 individuals from 12 RCTs were included (303 under IV sedation and 327 with IAL).
2. Between IAL and IV sedation, there was no difference in reduction success, no difference in adverse events, no difference in the length of stay in the ED, no difference in pain scores following analgesia, and no difference in the ease of reduction.
In conclusion, with fewer side effects, a shorter duration of stay in the ED, and no difference in pain scores or ease of reduction, intra-articular lidocaine may be as effective as IV sedation in successfully reducing anterior shoulder dislocations in the emergency department. When IV sedation is neither recommended or practical, intra-articular lidocaine may be a good substitute for it in order to reduce anterior shoulder dislocations.
Reference:
Sithamparapillai, A., Grewal, K., Thompson, C., Walsh, C., & McLeod, S. (2022). Intra-articular lidocaine versus intravenous sedation for closed reduction of acute anterior shoulder dislocation in the emergency department: a systematic review and meta-analysis. In Canadian Journal of Emergency Medicine. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43678-022-00368-z
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


