- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Low-dose prednisolone effective in patients with established rheumatoid arthritis: study
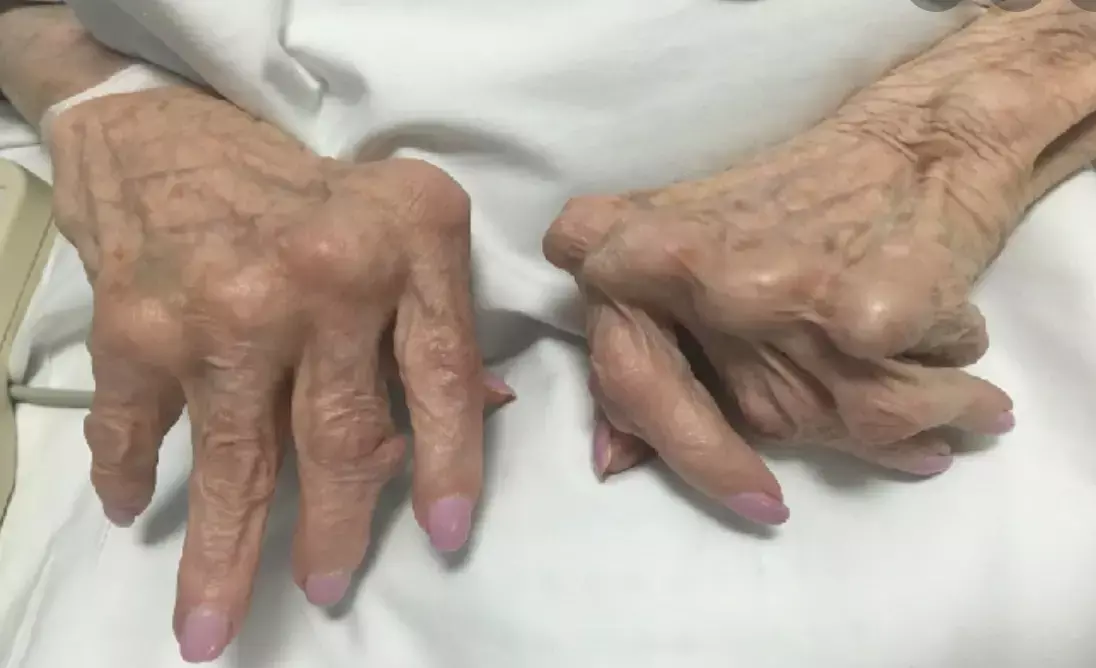
According to a recent study published in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, low-dose prednisolone is effective in treating patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatoid arthritis or RA is an autoimmune and inflammatory disease; This means that your immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in your body, causing inflammation (painful swelling) in the affected areas of the body. RA mainly attacks the joints, often many joints at once.
Low-dose glucocorticoid (GC) therapy is widely used in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), but the balance of benefit and harm is still unclear.
The GLORIA (Glucocorticoid LOW dose in Rheumatoid Arthritis) pragmatic double-blind randomized study compared 2 years of prednisolone, 5 mg/day to placebo in patients over 65 years of age with active RA. We allowed all co-treatments except long-term open-label GC and elderly-specific minimized exclusion criteria. Benefit outcomes included disease activity (disease activity score; DAS28, secondary) and joint damage (Sharp/van der Heijde, secondary). The other secondary outcome was harm, expressed as the proportion of patients with ≥1 adverse event (AE) of special interest. Such events include serious events, GC-specific events, and interruption events. Longitudinal models analyzed data with one-sided testing and 95% confidence limits (95% CL).
Results:
• The investigators randomized 451 patients with established RA and mean comorbidity of 2.1, 72 years of age, 11 years of disease duration, and DAS28 4.5. 79% were receiving disease-modifying therapy, 14% biologic. 63% of prednisolone and 61% of placebo patients completed the study.
• Interruptions were due to AE (both 14%), active disease (3% vs. 4%), and other (including covid pandemic-related disease) (19% vs. 21%); The average working time was 19 months.
• Disease activity was 0.37 points lower in prednisolone; joint damage progression was 1.7 points lower.
• 60% versus 49% of patients experienced a harm outcome with an adjusted relative risk of 1.24, with the greatest contrast (mostly non-severe) infections.
• Other GC-specific events were rare.
Therefore, additional low-dose prednisolone has long-term beneficial effects in elderly patients with established RA, mostly a tradeoff of 24% in patients with non-severe AE; this indicates a positive balance of benefit and harm.
Reference:
Boers M, Hartman L, Opris-Belinski D For the GLORIA Trial consortium, et alLow dose, add-on prednisolone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis aged 65+: the pragmatic randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled GLORIA trialAnnals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2022;81:925-936.
Keywords:
Low dose, add-on, prednisolone, patients, rheumatoid, arthritis, aged 65, pragmatic, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, GLORIA, trial, Maarten Boers, Linda Hartman, Daniela Opris-Belinski, Reinhard Bos, Marc R Kok, Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


