- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Low Vitamin D levels associated with poor rehabilitation outcomes after hip fracture: Study
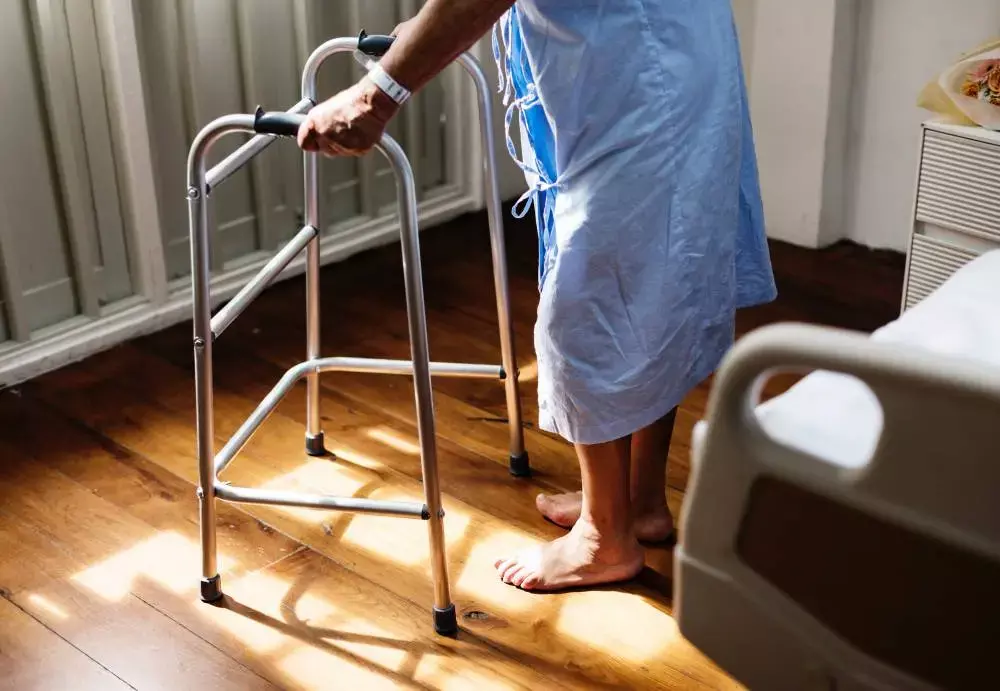
Vitamin D levels are associated with rehabilitation outcomes in post-acute hip fractured patients, suggests a study published in the journal Disability.
Therefore a routine screening for 25(OH)D levels and standardized supplementation protocol during the acute and post-acute rehabilitation setting is recommended as it may improve the quality of care.
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects.
A group of researchers from Israel conducted a study to report on serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) levels in post-acute hip fractured patients.
A retrospective study was conducted from September 2017 to September 2019 of 493 hip fractured patients. 25(OH)D levels were recorded following the patient's baseline characteristics and outcome measures, including the functional independence measure and motor functional independence measure effectiveness. The sample was divided into three groups: deficient (<30 nmol/l), insufficient (30–75 nmol/l) and sufficient (>75 nmol/l) 25(OH)D levels. ANOVA and chi-square test tests compared the groups. Multiple linear analysis assessed the associations between the 25(OH)D and discharge functional independence measure score.
The results of the study are as follows:
· 25(OH)D deficiency was found in 20.3% of the patients.
· The only baseline characteristic significantly associated with serum 25(OH)D levels was dementia.
· The group with deficient levels of 25(OH)D exhibited a significantly higher rate of low education, low admission albumin levels and a reduced handgrip strength compared to the insufficient/sufficient groups.
· All functional measure scores were significantly lower in the deficient (25(OH)D) group compared with the insufficient/sufficient patient groups. 25(OH)D levels were found to be significantly associated with the discharge functional independence measure score.
Thus, the researchers concluded that as 25-hydroxyvitamin D 25(OH)D levels are associated with rehabilitation outcomes in post-acute hip fractured patients; routine screening for 25(OH)D levels is mandatory in post-acute hip fracture patients as it may affect rehabilitation outcomes.
Reference:
Vitamin D levels in post-acute hip fractured patients and their association with rehabilitation outcomes by Hershkovitza A et. al published in the Disability and Rehabilitation.
https://doi.org/10.1080/09638288.2021.1971304
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


