- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Patients with hypothyroidism more prone to complications than euthyroid patients following TKA
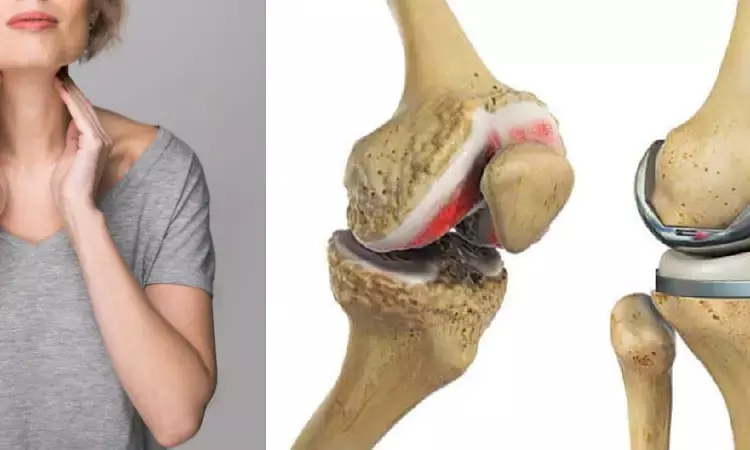
The number of hypothyroidism patients undergoing total knee replacement (TKA) in India is increasing. It is assumed that patients with hypothyroidism are more prone to complications following surgery. V. Ratnakar et al conducted a study to evaluate the impact of hypothyroidism on the complications following TKA. The study has been published in “Indian Journal of Orthopaedics”
A case–control analysis of patients who underwent primary total knee replacement was included in the study. Patient is considered hypothyroid when TSH levels are more than 5.60 mIU/mL or patients who were diagnosed hypothyroidism previously and were on treatment with thyroxin. Age, sex, BMI, pre-operative hemoglobin, blood trans fusion required, pre-operative and post-operative serum sodium levels, length of hospital stay, wound complications (like delayed wound healing, superficial surgical site infection, PJI), DVT and Pulmonary embolism within 90 days of index surgery were retrieved from institutional records. For hypothyroid patients, duration of hypothyroidism, dose of thyroid medication and pre-operative TSH levels were retrieved from records.
Key findings of the study were:
• A total of 600 patients were analyzed (Hypothyroid group n = 300, Control group n = 300).
• The mean age was 61.15 years in patients with hypothyroid and 61.34 in the control group.
• In both groups female preponderance was major.
• The medical complications were found to be 6.2% in the hypothyroid group compared to 4% in control group (p = 1.66, odds ratio 0.61).
• Surgical complications in the hypothyroid group were 3% compared to 0.6% in control group (p = 4.53, odds ratio = 0.21), overall complication rates were not significant statistically when compared between hypothyroid and control group (p = 5.01, odds ratio 0.47).
• Subgroup analysis of complications of hypothyroid patients with euthyroid status versus uncontrolled hypothyroidism was done and found no statistical difference in complications.
“The conclusion is that the rate of hospital stay, surgical site infections and complications were higher in hypo thyroid group when compared with control group though statistically not significant” the authors commented.
Further reading:
Effect of Hypothyroidism on Complications in Patients Undergoing TKA in Indian Population
V. Ratnakar, Sawankumar Pawar et al
Indian Journal of Orthopaedics (2023) 57:673–678
https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-023-00841-6
MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS
Dr Supreeth D R (MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS) is a practicing orthopedician with interest in medical research and publishing articles. He completed MBBS from mysore medical college, dip ortho from Trivandrum medical college and sec. DNB from Manipal Hospital, Bengaluru. He has expirence of 7years in the field of orthopedics. He has presented scientific papers & posters in various state, national and international conferences. His interest in writing articles lead the way to join medical dialogues. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


