- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Shear wave elastography a valuable tool for diagnosing and grading carpal tunnel syndrome: study
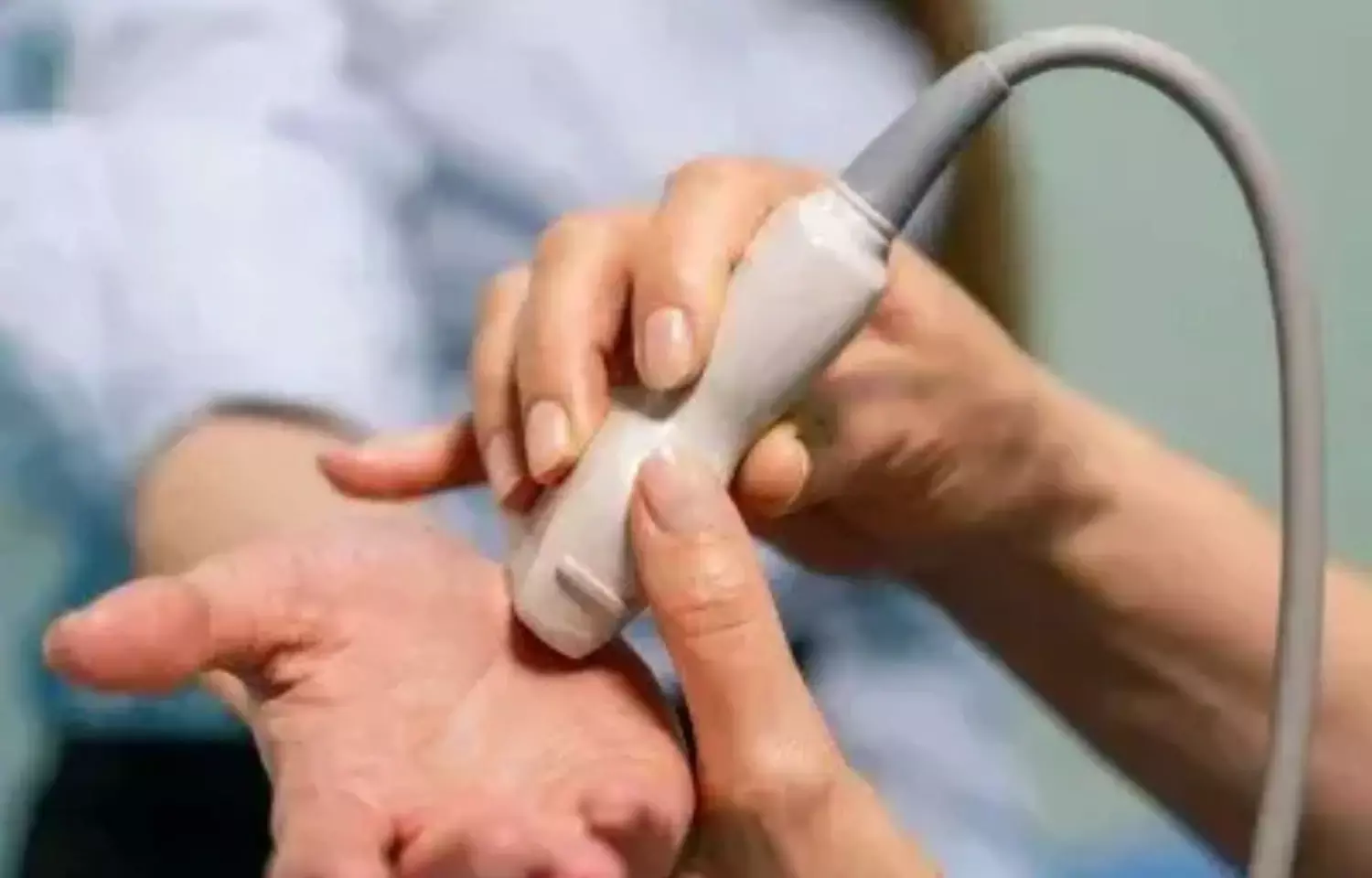
Renato Antonio Sernik et al conducted a study to quantify the shear velocity and stiffness of the median nerve (MN) with shear wave elastography (SWE) at the carpal tunnel entrance and determine whether SWE is useful for diagnosing and staging carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS).The authors found that - MN shear velocity and stiffness are significantly higher in CTS patients. SWE can be used to diagnose CTS and distinguish between patients with mild and severe disease.
Diagnosis and grading of CTS are based on a combination of clinical symptoms and electrophysiological abnormalities. However, electro diagnostic tests (EDTs) are invasive and uncomfortable for patients, and false negatives occur in up to 10–20% of cases.
Shear wave elastography (SWE) is an US technique that quantifies neural tissue stiffness by measuring the speed and pattern of shear wave propagation expressed as a quantitative parameter in either meters per second (m/s) or kilopascals (kPa). The elastic shear stiffness of a material is called the shear modulus; the shear velocity represents the velocity at which shear waves propagate through matter and is also representative of a tissue's elasticity.
The study included 58 patients (79 wrists) with clinical and electroneuromyographic diagnoses of CTS and 55 healthy controls (63 wrists). An experienced radiologist with 20 years of experience in musculoskeletal US (US) examined the entire patient and control groups with grayscale US and SWE. The radiologist was blinded to the individual's group at the time of examination. MN shear velocity and stiffness were measured by SWE on the axial plane in both groups. The differences between CTS patients and controls and between different grades of CTS based on electro diagnostic tests were studied using Student's t test and ANOVA with ROC analysis.
The results of the study were:
The mean MN shear velocity and stiffness were significantly greater in CTS patients (2.5 ± 0.37 m/s and 19.4±5.8 kPa) than in controls (1.91±0.24 m/s and 11.1±3.0 kPa) (p < 0.001) and greater in the severe CTS group (2.69±0.39 m/s and 22.4±7.1 kPa) than in the mild CTS group (2.37 ± 0.35 m/s and 17.3 ± 4,8 kPa).
The cutoff value for the shear velocity was 2.13 m/s, with 86% and 82% sensitivity and specificity, respectively, and the cutoff value for stiffness was 13.6 kPa, with 87% and 82% sensitivity and specificity.
The authors concluded that - SWE of the MN in the transverse plane can be used for the diagnosis and staging of CTS. A cutoff value of 2.13 m/s for shear velocity and 13.6 kPa for shear modulus of the MN measured in the transverse plane at the carpal tunnel inlet better correlate with CTS diagnosis, while values of 2.6 m/s for shear velocity and 19.6 kPa for shear modulus showed significance for distinguishing patients with severe disease.
Key Words: Median nerve, Shear wave, Elastography, Neuropathy, Ultrasound, Axial plane, Skeletal Radiology, Renato Antonio Sernik.
Further reading:
Shear wave elastography is a valuable tool for diagnosing and grading carpal tunnel syndrome
Renato Antonio Sernik et al
Skeletal Radiology
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-022-04143-0
MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS
Dr Supreeth D R (MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS) is a practicing orthopedician with interest in medical research and publishing articles. He completed MBBS from mysore medical college, dip ortho from Trivandrum medical college and sec. DNB from Manipal Hospital, Bengaluru. He has expirence of 7years in the field of orthopedics. He has presented scientific papers & posters in various state, national and international conferences. His interest in writing articles lead the way to join medical dialogues. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


