- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Tibial component overhang of more than 3 mm medially increases risk of short-term postoperative revision in UKA
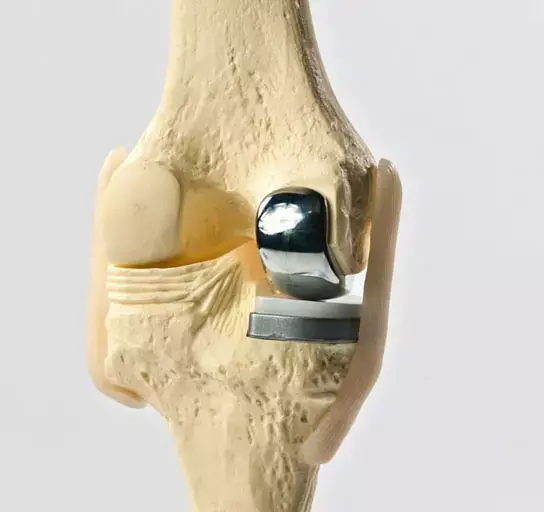
Although Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty (UKA) has many advantages, the literature has shown that UKA has a higher revision rate than total knee arthroplasty (TKA). Common reasons for revision in UKA are knee pain, aseptic loosening of the component, progression of contralateral knee osteoarthritis, and bearing wear/dislocation. Some studies have shown that the position of the tibial component in Oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with a mobile bearing will affect the clinical outcome of patients. Hence, Kanglong Wu et al conducted a study to investigate the relationship between the overhang distance of the tibial component and the survival of the implant.
A retrospective analysis of patients who underwent unicompartmental knee arthroplasty was done. The study was divided into three groups:
minor underhang group (underhang between -3 and 0 mm);
minor overhang group (overhang 0–3 mm); and
major overhang group (overhang >=3 mm).
Demographic and clinical profile characteristics of each group were compared and survival curves of each group were also compared using Kaplan–Meier and modeled using multivariate Cox regression.
Key findings of the study were:
• A total of 351 knees were included in this study with a minimum follow up of three years and a mean follow up of 4.8 ± 1.5 years.
• The revision rates in each group were 3.6% (minor underhang group), 2.7% (minor overhang group), and 20.9% (major overhang group) (P < 0.001).
• From the three groups’ cumulative survival rates, the major overhang group was significantly lower than the other two groups (log rank P < 0.001).
• Multivariate Cox regression showed an association between the major overhang group and implant survival rate (hazard ratio = 7.515, 95% confidence interval = 2.500–22.593, P < 0.001).
The authors concluded that – “This study found that a tibial component overhang of more than 3 mm medially increases the risk of short-term postoperative revision in UKA. The reasons for revision are generally bearing dislocation and aseptic loosening. Therefore, we recommend that surgeons should try to keep the overhang distance of tibial component relative to the tibial plateau to within 3 mm.”
Further reading:
Effect of tibial component overhang on survivorship in medial mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty
Kanglong Wu, Guoqi Lv et al
The Knee 37 (2022) 188–195
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knee.2022.06.011
MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS
Dr Supreeth D R (MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS) is a practicing orthopedician with interest in medical research and publishing articles. He completed MBBS from mysore medical college, dip ortho from Trivandrum medical college and sec. DNB from Manipal Hospital, Bengaluru. He has expirence of 7years in the field of orthopedics. He has presented scientific papers & posters in various state, national and international conferences. His interest in writing articles lead the way to join medical dialogues. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


