- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
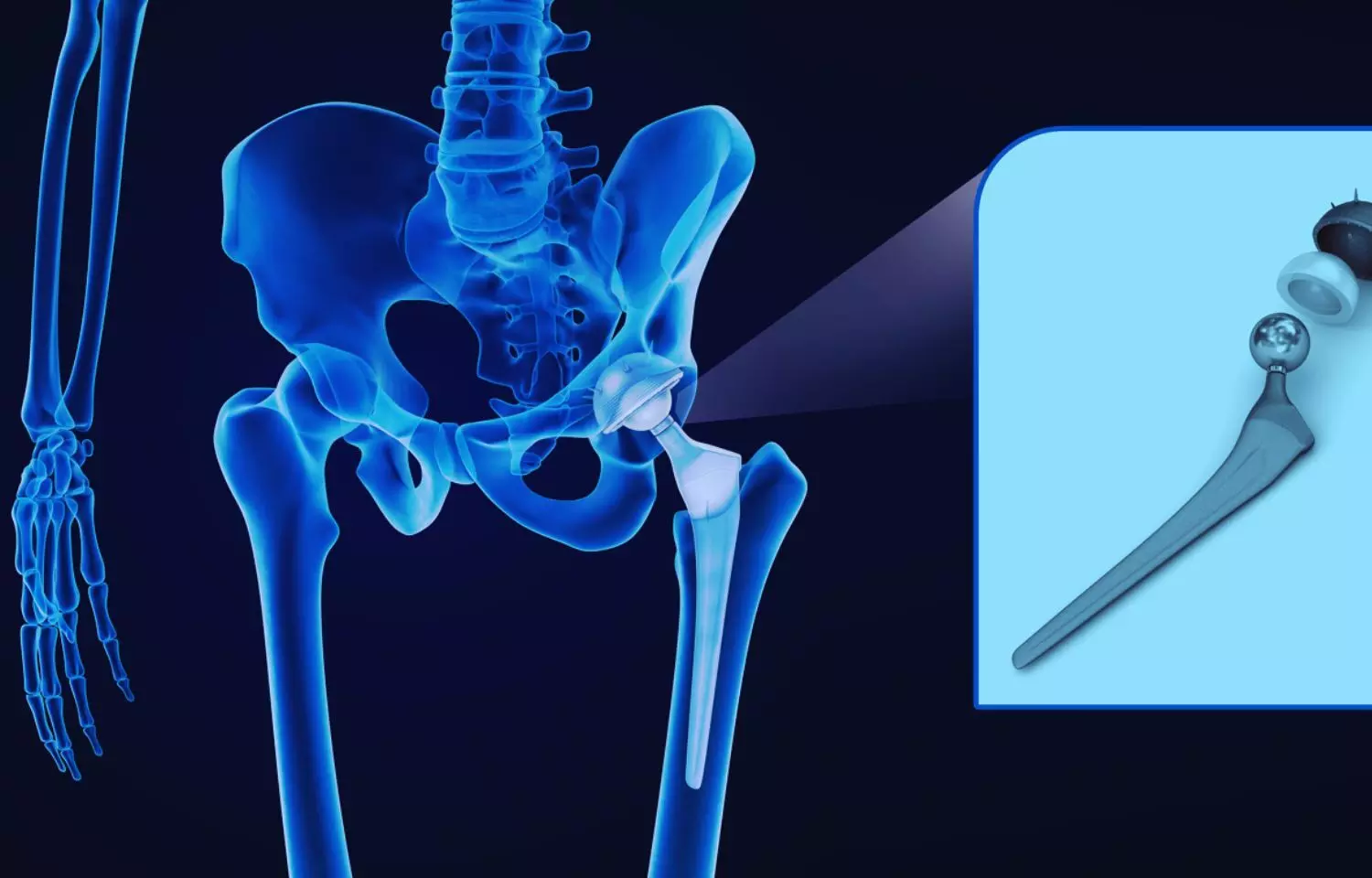
Total Hip Surgery more effective than Resistance Training in Hip Osteoarthritis: Study
A recent study found that total hip surgery substantially reduced hip pain and clinically relevant improvement in hip function than resistance training. This observation was seen in individuals aged 50 years and older suffering from hip osteoarthritis as published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Hip osteoarthritis is a common disability disorder in old age causing pain, functional impairment, and reduced quality of life. Total hip replacement surgery is a routine procedure for individuals with hip osteoarthritis. Non-surgical procedures like resistance training are one of the common procedures prescribed. However, there is uncertainty in the previous literature on the effectiveness of total hip surgery over resistance training. Hence, researchers from Denmark conducted a trial to evaluate whether total hip replacement would provide superior results regarding alleviation of patient-reported hip pain and improved patient-reported function as compared with resistance training.
A multicenter, randomized, controlled, superiority trial was carried out by randomly (1:1) assigning the individuals to undergo total hip replacement or to participate in a supervised resistance training program using a computer-generated randomization sequence. Individuals aged 50 years or older who had severe hip osteoarthritis and an indication for total hip replacement based on hip pain, clinical presentation, and radiographic imaging were included in the trial. The total hip surgery included a standard fast-track surgical program while the resistance training included 1-hour, individual, supervised sessions twice weekly for 12 weeks. After the initiation of the trial, follow-ups were carried out at 3, 6, 12, and 24 months. The primary outcome was the change in patient-reported hip pain and function from baseline to 6 months as assessed using the Oxford Hip Score. Secondary outcomes included changes from baseline to 6 months in patient-reported domains of pain, symptoms, function in activities of daily living, hip-related quality of life, and function in sports and recreation.
Findings:
- A total of 109 patients (mean age, 67.6 years) were randomly assigned to total hip replacement (53 patients) or resistance training (56 patients).
- An improvement (mean increase) was seen in the Oxford hip score by 15.9 points in total hip replacement and 4.5 points in the resistance training group in the intention-to-treat analysis.
- The total hip replacement group has shown a significant improvement over the resistance training group in the intent-to-treat analysis.
- From baseline to 6 months, 5 patients (9%) who had been assigned to total hip replacement had not undergone surgery, and 12 patients (21%) who had been assigned to resistance training had undergone total hip replacement.
- The incidence of serious adverse events at 6 months was similar in the two groups; the majority of such events were known complications of total hip replacement.
Thus, the study concluded that total hip replacement resulted in a clinically important, superior reduction in hip pain and improved hip function in individuals aged 50 years and older with hip osteoarthritis.
Further reading: Frydendal T, Christensen R, Mechlenburg I, et al. Total Hip Replacement or Resistance Training for Severe Hip Osteoarthritis. N Engl J Med. 2024;391(17):1610-1620. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2400141
BDS, MDS
Dr.Niharika Harsha B (BDS,MDS) completed her BDS from Govt Dental College, Hyderabad and MDS from Dr.NTR University of health sciences(Now Kaloji Rao University). She has 4 years of private dental practice and worked for 2 years as Consultant Oral Radiologist at a Dental Imaging Centre in Hyderabad. She worked as Research Assistant and scientific writer in the development of Oral Anti cancer screening device with her seniors. She has a deep intriguing wish in writing highly engaging, captivating and informative medical content for a wider audience. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751