- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Ultrasound detects significantly low crystal deposition in gout by ULT: Study
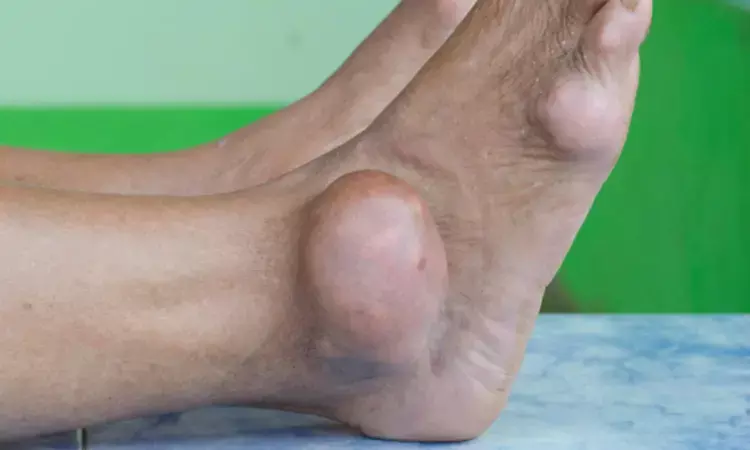
Norway: A treat-to-target approach with urate lowering therapy caused a significant reduction of ultrasound-detected crystal depositions after 12 months in gout patients, according to a recent study in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. Further, an ultrasound scoring system for crystal depositions was found to be sensitive to change.
Ultrasound is sensitive to changes for the detection of crystal deposition in gout patients. Hilde Berner Hammer, Department of Rheumatology, Diakonhjemmet Sykehus, Oslo, Norway, and colleagues explored the main locations for depositions and the extent of dissolution of depositions during a treat-to-target approach with urate-lowering treatment (ULT) in gout patients.
This single-center study consecutively included patients with a recent flare of gout. Thye were manged by a treat-to-target approach with ULT. The patients were assessed at baseline, 3, 6, and 12 months including bilateral ultrasound examinations of joints/tendons/entheses of hands, elbows, knees, ankles, and feet. During follow-up, the number of depositions were quantified by applying a new semiquantitative scoring system of 0–3 of elementary lesions (double contour (DC), tophi, and aggregates).
209 of the patients were evaluated with ultrasound at baseline (mean (SD) age 56.4 (13.8) years and disease duration 7.9 (7.7) years, 95.2% were men).
Key findings of the study include:
- The serum urate levels decreased from baseline to 12 months (mean (SD) 500 (77) to 312 (49) µmol/L)).
- The first metatarsophalangeal joint was the most frequent location for all the elementary lesions and erosions were associated with higher levels of crystal depositions.
- From baseline to 12 months, mean sum scores decreased for DC (4.3 to 1.3), tophi (6.5 to 3.8) and aggregates (9.3 to 6.7), with DC being most sensitive to change.
"The ultrasound scoring system for crystal depositions was sensitive to change and showed that a treat-to-target approach with ULT resulted in significant reductions of all the depositions, most extensively for DC," concluded the authors.
For further reference log on to:
Hammer HB, Karoliussen L, Terslev L, Haavardsholm EA, Kvien TK, Uhlig T. Ultrasound shows rapid reduction of crystal depositions during a treat-to-target approach in gout patients: 12-month results from the NOR-Gout study. Ann Rheum Dis. Published online July 15, 2020. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217392
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


