- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Upadacitinib Monotherapy Hampers Joint Damage in RA: Study
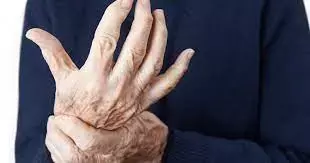
Upadacitinib monotherapy is beneficial in inhibiting structural joint damage progression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, according to a recent study published in the Rheumatology.
A study was conducted to evaluate the inhibition of progression of structural joint damage through week 48 in patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) receiving upadacitinib as monotherapy or in combination with methotrexate.
Radiographic progression was assessed in two phase 3 randomized-controlled trials. Methotrexate-naïve patients were randomized to upadacitinib 15 or 30 mg once daily (QD) or methotrexate monotherapy (SELECT-EARLY, n = 945), while methotrexate inadequate responders (IR) were randomized to upadacitinib 15 mg QD or adalimumab 40 mg every other week or placebo added to background methotrexate (SELECT-COMPARE, n = 1629). Mean changes from baseline in modified Total Sharp Score (mTSS), joint space narrowing (JSN), and erosion scores (ES) were determined. Data were analysed both by linear extrapolation for missing data imputation and treatment switching and as-observed.
Results:
In patients naïve or with limited exposure to methotrexate (SELECT-EARLY), mean changes from baseline to week 48 in mTSS were 0.03 for upadacitinib 15 mg, 0.14 for upadacitinib 30 mg, and 1.00 for methotrexate based on linear extrapolation (p < 0.001 for both upadacitinib doses vs methotrexate). Among patients with an inadequate response to methotrexate (SELECT-COMPARE), the mean change from baseline in mTSS was significantly reduced in the upadacitinib 15 mg plus methotrexate group vs placebo plus methotrexate (0.28 vs 1.73; p < 0.001); mean change from baseline in the adalimumab plus methotrexate group was 0.39.
Upadacitinib monotherapy or in combination with background methotrexate was effective in inhibiting the progression of structural joint damage through week 48 in methotrexate-naïve and methotrexate-IR patients with RA.
Reference:
Peterfy CG, Strand V, Friedman A, et al. Inhibition of Structural Joint Damage Progression with Upadacitinib in Rheumatoid Arthritis: 1-Year Outcomes from the SELECT Phase 3 Program [published online ahead of print, 2021 Dec 13]. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;keab861. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keab861
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


