- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Wearable sleeves show promise for clinical knee & elbow ROM measurement and remote monitoring: study
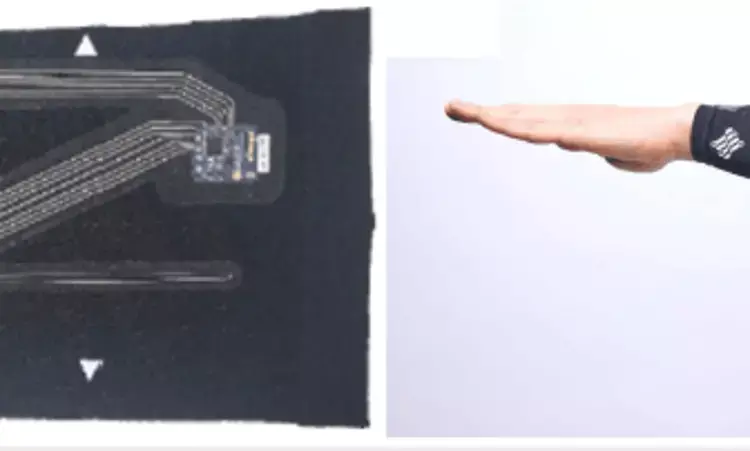
Goniometers are a common clinical tool for measuring joint range of motion. Wearable sleeves offer a novel and alternative method to measure joint angles, record range of motion (ROM), and remotely track changes in ROM over time. Additionally, they may aid in the surgical planning required for deformity correction. This investigation compared the reliability and validity of a conventional goniometer to a novel transducer embedded sleeve when measuring flexion and extension of the elbow and knee.
Neufeld E V et al conducted a cross-sectional study of 55 patients (110 elbows, 110 knees) who donned an elbow and knee sleeve embedded with a gallium-based strain sensor. Flexion and extension of the elbow and knee were measured both manually using a goniometer and a wearable sleeve. Agreement between the two devices was assessed via Bland-Altman plots.
The key findings of the study were:
• Regarding elbow flexion, the bias observed between the two devices was 4.6° with LoA spanning from -14.9° to 24.1°. Regarding elbow extension, the bias observed between the two devices was -9.8° with LoA spanning from -25.6° to 6.0°.
• Regarding knee flexion, the bias observed between the two devices was -4.6° with LoA spanning from -35.6° to 26.4°. Regarding knee extension, the bias observed between the two devices was - 2.8° with LoA spanning from -8.9° to 3.3°.
The authors concluded – “The proprietary sleeve investigated in this study demonstrated significant systematic bias relative to the traditional goniometer; therefore, the sleeve needs refinement, and thus, we cannot recommend that it be utilized in the clinical setting at this time. While the device shows some promise, primarily for measuring knee extension, it currently requires substantial refinement before it can obviate the need for the traditional goniometer. Part of this bias may be due to the challenges faced in consistent sleeve placement around the joint. Most importantly, improvements in product development should focus on optimizing the sleeve fit and the reproducible positioning of the strain sensor to address the user-interface challenges present in the current study. Consistent and precise sleeve placement should enhance clinical utility. Further research must demonstrate validity in not only healthy patients but also those with joint pathologies, such as osteoarthritis and ligamentous insufficiency, and include a larger sample size. This study serves as a valuable foundation for this technology, pointing to the possibility that with reduced bias, wireless sleeves may present a new, less cumbersome alternative for measuring joint ROM.”
Further reading:
Agreement Between a Wireless Sleeve and a Goniometer in Measuring Elbow and Knee Range of Motion, Eric V. Neufeld et al Cureus 17(9): e91748. DOI 10.7759/cureus.91748
MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS
Dr Supreeth D R (MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS) is a practicing orthopedician with interest in medical research and publishing articles. He completed MBBS from mysore medical college, dip ortho from Trivandrum medical college and sec. DNB from Manipal Hospital, Bengaluru. He has expirence of 7years in the field of orthopedics. He has presented scientific papers & posters in various state, national and international conferences. His interest in writing articles lead the way to join medical dialogues. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.


