- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
USG guided multisite injection technique for nonsurgical treatment of Frozen Shoulder serves better analgesia
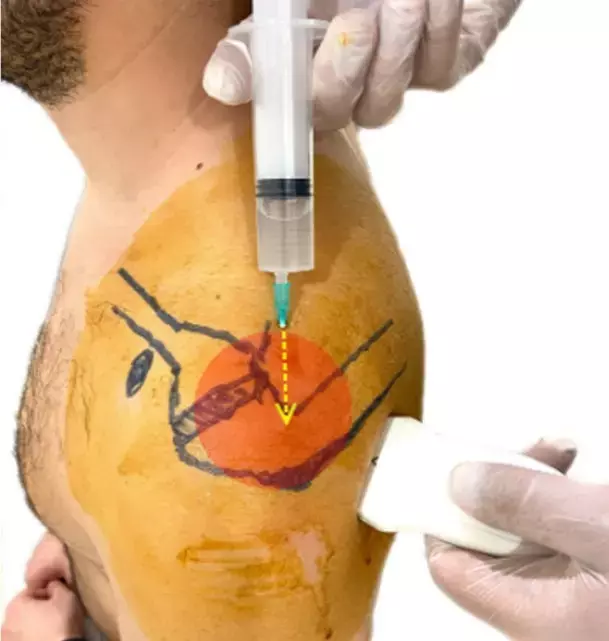
Frozen shoulder (FS) is an elusive condition that affects patients' mental and emotional quality of their lives. Corticosteroid injection technique is one of the first-line treatment methods in the treatment of FS. Ultrasound (USG) guidance allows visualization of the shoulder anatomy and improves the accuracy of the injection site.
Emre Koraman et al described an USG-guided injection technique for FS treatment. The aim of this technique is to affect glenohumeral joint and capsule, subacromial space, the long head of biceps tendon sheath, and the coracohumeral ligament. For this purpose, four different sites were injected by USG guidance.
The patient sits in an upright position with their hands positioned on their thighs. Bony landmarks, including clavicle, spina scapulae, acromion, and coracoid process, are identified and marked. At first, ultrasonographic examination is performed. In the multisite injection technique, a total of 40-ml drug solution, consisting of 2 mL of triamcinolone acetonide (40 mg/mL), 4 mL bupivacaine (0.5%), and 34 mL saline solution is prepared. After cleaning the skin with povidone-iodine, the injections are performed in a sterile manner. A 23-gauge needle is inserted parallel to the transducer in a semi-oblique plane from the posterior side of the shoulder. The needle is advanced under real-time USG guidance until the needle tip enters the glenohumeral joint.
At this point, 5 mL of the solution is injected into the glenohumeral joint, and 5 mL is injected into the outer surface of the postero-inferior capsule. 10mL of drug combination is applied to the postero-superior capsule from 2 cm cephalous to the midpoint of the spina scapulae by directing the tip of the syringe from the supraspinatus fossa to the under surface of the acromion, while the joint capsule is screening posteriorly by the transducer. The expansion of the joint capsule is checked while the solution is being injected.
For the SA injection, lateral approach is used in which the long axis of the supraspinatus is the parallel to the probe, and the needle is inserted parallel or oblique in relation to the probe.10mL of the drug combination is injected to the SA space, while visualizing it on the screen.
Finally, the long head of biceps (LHB) tendon sheath and coracohumeral ligament are identified in the transverse plane by USG; perpendicular to the long axis, the needle is inserted in-plane with the probe into the lateral and inferior aspect of the LHB tendon sheath and coracohumeral ligament. The needle tip position can be checked with a small amount of injected solution and 10-mL drug combination is applied to the LHB tendon sheath and around the coracohumeral ligament.
Patients are observed for 30 minutes for any possible side effects, including local bleeding, weakness, anaphylaxis, motor deficiencies, and/or vasovagal reactions. Each participant should be checked for late side effects. Patients are participated in a standard physiotherapy program within the first 2 hours after injection. Physiotherapy is performed in every other day for 6 sessions in total. During the physiotherapy program, glenohumeral joint, scapulothoracic joint, acromioclavicular joint mobilization; capsule stretching exercises; and soft tissue mobilization were performed. Patients are provided a home exercise program consisting of stretching exercises and movements to preserve their ROM.
The authors commented - "The multisite injection technique is presented for the nonsurgical treatment of FS, emphasizing correct injection sites. This will provide better analgesia, better ROM, and better functional results in the treatment of patients with FS."
Further reading:
Ultrasound Guided Multisite Injectıon Technique in the Treatment of Frozen Shoulder Emre Koraman, Ismail Turkmen et al Arthroscopy Techniques, Vol 11, No 10 (October), 2022:1823-1826 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eats.2022.06.02
MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS
Dr Supreeth D R (MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS) is a practicing orthopedician with interest in medical research and publishing articles. He completed MBBS from mysore medical college, dip ortho from Trivandrum medical college and sec. DNB from Manipal Hospital, Bengaluru. He has expirence of 7years in the field of orthopedics. He has presented scientific papers & posters in various state, national and international conferences. His interest in writing articles lead the way to join medical dialogues. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


