- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Abnormal brain MRI findings in infants with mild neonatal encephalopathy
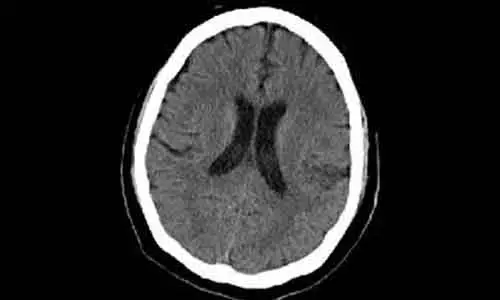
Researchers from a recent study have found out that 18% of infants with mild encephalopathy had an abnormal short-term outcome, such as abnormal brain magnetic resonance imaging findings.
The study is published in the BMC Pediatrics Journal.
Neonatal encephalopathy due to acute perinatal asphyxia is a major cause of perinatal brain damage. Moderate to severe neonatal encephalopathy is associated with high mortality and morbidity rates. However, the neurodevelopmental outcomes in neonates with mild neonatal encephalopathy are unclear.
Hence, Yoshinori Aoki and colleagues from the Department of Neonatology, Tokyo Metropolitan Children's Medical Center, Tokyo, Japan carried out this single-center observational study was to assess the short-term outcomes in term neonates with mild neonatal encephalopathy due to perinatal asphyxia.
A secondary aim of the study was to identify predictors of poor prognosis by identifying the characteristics of these infants according to their short-term outcomes.
The investigators retrospectively accessed all infants with perinatal asphyxia at Tokyo Metropolitan Children's Medical Center. In total, 110 term infants with perinatal asphyxia during the study period were screened and 61 were diagnosed with mild neonatal encephalopathy.
An abnormal short-term outcome was defined as any one of the following: seizures or abnormal electroencephalography, abnormal brain magnetic resonance imaging obtained within the first 4 weeks of life, and abnormal neurological examination findings at discharge.
The following results were observed-
a. Eleven (18 %) of these infants had an abnormal short-term outcome.
b. The median Thompson score at admission was significantly higher in infants with abnormal short-term outcomes than in those with normal short-term outcomes (5 [interquartile range, 4-5.5] vs. 2 [interquartile range, 1–3], p < 0.01).
c. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis showed that a cutoff value of 4 had high sensitivity and specificity (90.9 and 83.0 %, respectively) for the prediction of an abnormal short-term outcome.
Therefore, the authors concluded that "18 % of infants with mild encephalopathy had an abnormal short-term outcome, such as abnormal brain magnetic resonance imaging findings. The Thompson score at admission may be a useful predictor of an abnormal short-term outcome in infants with mild neonatal encephalopathy."
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


