- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Long Peripheral Catheters first-line device for for Multiday IV Therapy in kids: Study
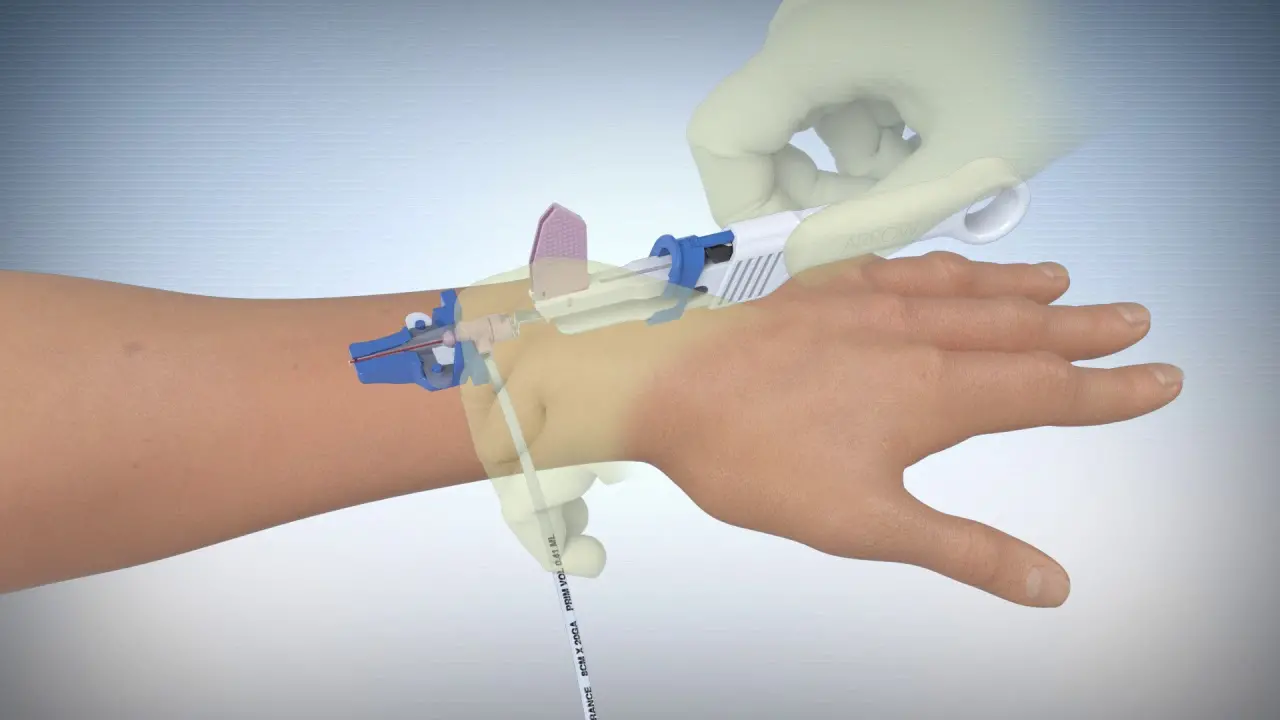
Establishment of functioning peripheral intravenous (IV) access is a vital step to provide care in the emergency and inpatient settings. A recent study suggests that Long Peripheral Catheters (LPCs) reduces catheter failure and total catheters in children and recommend the use of LPCs as the first-line device for peripheral access. The study findings were published in the journal PEDIATRICS on January 14, 2021.
Patients with a medical history of obesity, IV drug abuse (IVDA), end-stage renal disease (ESRD), and/or sickle cell disease have been shown to have Difficult Vascular Access (DVA) using the traditional technique. Once cannulated, the survival time of IV catheters is problematic, with early failure a common complication. In children, intravenous therapy (IVT) is generally administered via peripheral intravenous catheters (PIVCs) (2–6 cm in length). However, a previous study suggests that PIVCs are unreliable after 2 days. Long peripheral catheters (LPCs) (6–15 cm in length) could improve the delivery of IVT, but the data available are limited. Therefore, researchers of Melbourne, Australia, conducted a study to determine if LPCs could decrease catheter failure and the number of catheters in children receiving multiday IVT.
It was an open-label randomized controlled trial conducted at Monash Children's Hospital in Melbourne, Australia. Researchers included 72 participants of age1 to 17 years, undergoing surgery and requiring >48 hours of postoperative IVT. They randomly assigned them to receive either 2.5-cm 22G PIVCs (n=36) or 8-cm 22G LPCs (n=36).
Key findings of the study were:
• Upon analysis, researchers have found a similar median duration of IVT of 5.1 days between the groups.
• They also found that the catheter failure was higher for PIVCs than LPCs (66.7% vs 19.4% or 187.9 vs 41.0 failures per 1000 catheter-days).
• They noted that the infiltration was the most common reason for PIVC failure (33.3% vs 2.8%).
• They found that LPCs exhibited superior life span (4.7 vs 3.5 days) and children with LPCs were twice as likely to complete therapy with a single catheter (80.6% vs 38.9%).
The authors concluded, "LPCs reduce catheter failure and total catheters in children. They should be considered as the first-line device for peripheral access in any child receiving prolonged IVT".
For further information:
https://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/early/2021/01/13/peds.2020-000877
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


