- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Prehospital epinephrine may reduce biphasic reaction and decrease ED length of stay in pediatric anaphylaxis patients: Study
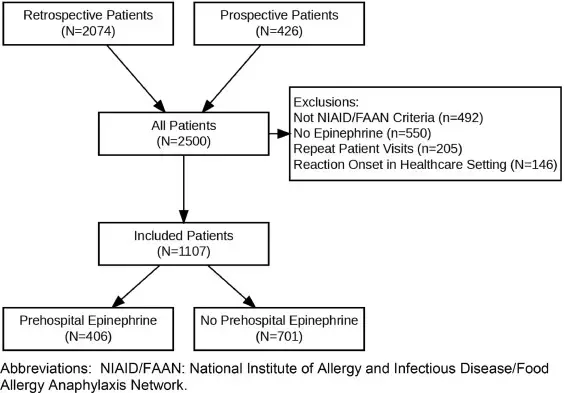
Prehospital epinephrine may reduce biphasic reaction and decrease ED length of stay in pediatric anaphylaxis patients suggests a study published in the Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology.
Prompt epinephrine administration is important to improve outcomes in anaphylaxis. The objective of our study was to assess the impact of prehospital epinephrine on clinical outcomes of hospital admission, biphasic reactions, and ED length of stay (LOS) in a cohort of ED anaphylaxis patients including both children and adults. They conducted a single-center prospective and retrospective cohort study of anaphylaxis patients from April 2008 to December 2022. Associations between prehospital epinephrine administration with biphasic reactions and ED LOS were assessed with univariable models and the association with ED disposition was assessed with both univariable and multivariable logistic regression.
Results: A total of 1107 patient visits were included for analysis. The median patient age was 29 (IQR 14-50), 593 (53.6%) patients were female, 366 (33.1%) were under 18 years of age. Patients in the prehospital epinephrine group were also less likely to experience a biphasic reaction (5.4% vs 9.3%; OR 0.56, 95% CI 0.34–0.92) and had a decreased ED LOS (median 4.0 hours vs 4.7 hours). There was no difference in hospital admission between patients with and without prehospital epinephrine in both the univariable (19.5% vs 15.7%; OR 1.30, 95% CI: 0.94–1.79) and multivariable (aOR 1.08, 95% CI: 0.71-1.64) models. Prehospital epinephrine administration reduced the odds of a biphasic reaction and decreased ED LOS but did not reduce hospitalization in this cohort of ED anaphylaxis patients. Our findings suggest that timely administration of prehospital epinephrine is associated with improved patient outcomes.
Reference:
Andrea L. Hlady, Aliza F. Weinman, Yuedan Zhang, Aidan F. Mullan, Ronna L. Campbell, Outcomes Associated with Prehospital Epinephrine in Adult and Pediatric Anaphylaxis Patients. Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. 2024. ISSN 1081-1206, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anai.2024.08.006.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


