- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Vitamin D supplementation has no effect on rickets or growth in stunted kids: Study
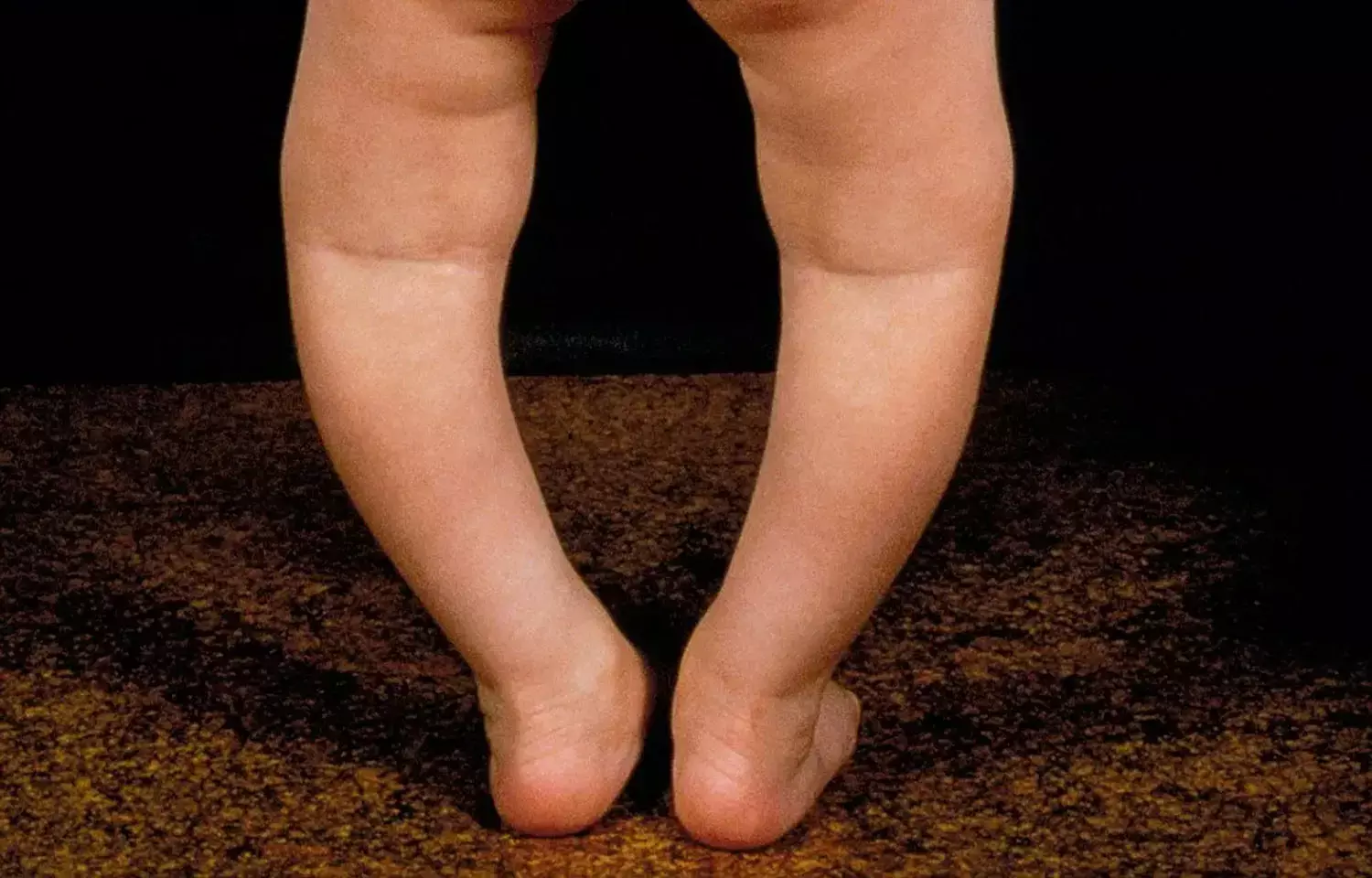
UK: Vitamin D supplementation has no effect on children with stunted growth or rickets except for those having high calcium intake, finds a recent study in the journal Pediatrics.
Vitamin D or sunshine vitamin is essential for healthy development of bones but not much is known about effects of vitamin D supplementation in young children with stunted growth. The aim of the study by Francesca L. Crowe, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, London, United Kingdom, and colleagues was to assess the effect of vitamin D supplementation on rickets risk and linear growth among Afghan children.
The double-blind, placebo-controlled trial included 304 children (aged 1 to 11 months) from Kabul. They were randomly assigned to receive oral vitamin D3 (100 000 IU) or placebo every 3 months for 18 months. Rickets Severity Score was calculated using knee and wrist radiographs for 631 randomly selected infants at 18 months. Rickets was defined as a score >1.5. Length and weight were measured at baseline and 18 months by using standard techniques, and z scores were calculated.
Key findings of the study include:
- Mean (95% confidence interval [CI]) serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (seasonally corrected) and dietary calcium intake were insufficient at 37 (35–39) nmol/L and 372 (327–418) mg/day, respectively.
- Prevalence of rickets was 5.5% (placebo) and 5.3% (vitamin D): odds ratio 0.96.
- The mean difference in height-for-age z score was 0.05, although the effect of vitamin D was greater for those consuming >300 mg/day of dietary calcium (0.14).
- There were no between-group differences in weight-for-age or weight-for-height z scores.
"Among the young Afghan children who were mostly calcium and vitamin D insufficient, there was no effect of vitamin D supplementation given every 3 months or 18 months on the rickets risk and growth except for those having a high calcium intake (who had a marginally better growth," wrote the authors.
"In future research studies of growth and rickets in undernourished children, researchers need to consider both the vitamin D dosing regimens as well as calcium supplementation," they concluded.
The study titled, "Vitamin D for Growth and Rickets in Stunted Children: A Randomized Trial," is published in the journal Pediatrics.
DOI: https://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/147/1/e20200815
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


