- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Angioedema a unique complication of mood stabilizer use, reports IJP study
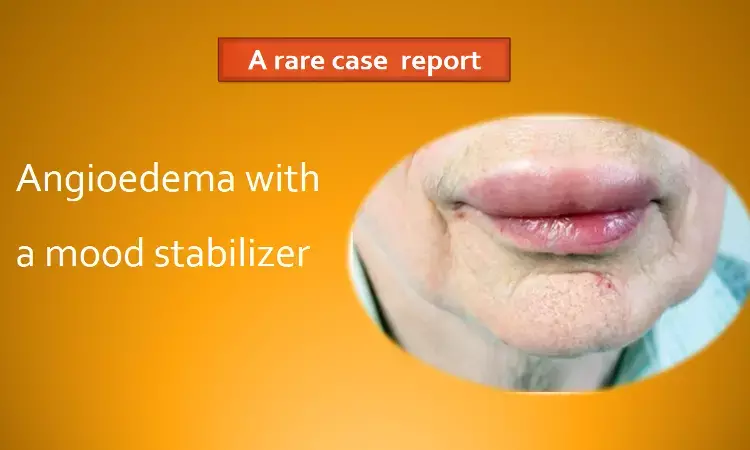
Angioedema is a sudden onset, life-threatening localized edema of the dermis. Incidence of this pathology with valproic acid has never been described before. A recent case report by Sevler Yildiz and Asli Kazgan published in Indian Journal of Psychiatry describes a unique complication of valproic acid in the form of angioedema in a patient of bipolar disorder.
A 30-year-old literate female patient diagnosed with bipolar disorder presented to the psychiatry department with a complaint of excessive activity, irritability, and insomnia that started 20 days before. Young Mania Scale (YMS) score was 31. The case was admitted with a prediagnosis of mood episode. The treatment was initiated with 250 mg/day valproic acid and 5 mg/day lorazepam, and valproic acid dose was increased to 1000 mg/day.
On the 5th day of the treatment unilateral periorbital swelling was noticed. The next day, swelling of the bilateral eyelids became evident, and the patient started to experience difficulty when opening her eyes. The erythema-free, painful edema gradually increased on the same day and spread to the face.
During this period, the patient did not use any additional medication or substance. The patient was diagnosed with angioedema during the requested dermatology consultation.
Valproic acid and lorazepam were discontinued. As an angioedema treatment, 2 × 40 mg/day prednisolone was diluted with 200 cc serum physiologic; intravenous was initiated with 2 × 40 mg/day pheniramine. After the treatment, the edema in the eye region and the face of the patient was reduced, and these symptoms disappeared on the 4th day. This condition was considered as valproic acid-induced angioedema, and the patient was followed up.
Ten milligram/ day olanzapine treatment, which has mood stabilizing properties, was initiated and the dose was gradually increased to 40 mg/day. The patient, whose psychiatric complaints decreased and YMS score decreased to 12, was discharged with 40 mg/day olanzapine prescription on the 25 th day of hospitalization. Angioedema was not observed in the subsequent follow-up.
Angioedema is a clinical diagnosis, with no required testing. "Angioedema induced by antiepileptic drugs such as carbamazepine and lamotrigine have been previously reported but no case of angioedema due to valproic acid treatment in a patient with bipolar disorder diagnosis has been reported", mention authors in the case discussion.
The present case demonstrated that skin reactions such as angioedema, which are of vital importance, may occur after the use of antiepileptics such as valproic acid, a nonaromatic antiepileptic.
Source: Indian Journal of Psychiatry: https://dx.doi.org/10.4103/indianjpsychiatry.indianjpsychiatry_1371_20
M.B.B.S, M.D. Psychiatry
M.B.B.S, M.D. Psychiatry (Teerthanker Mahavir University, U.P.) Currently working as Senior Resident in Department of Psychiatry, Institute of Human Behaviour and Allied Sciences (IHBAS) Dilshad Garden, New Delhi. Actively involved in various research activities of the department.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


