- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
ECT shows remarkable benefit in neuropathic pain, a case report
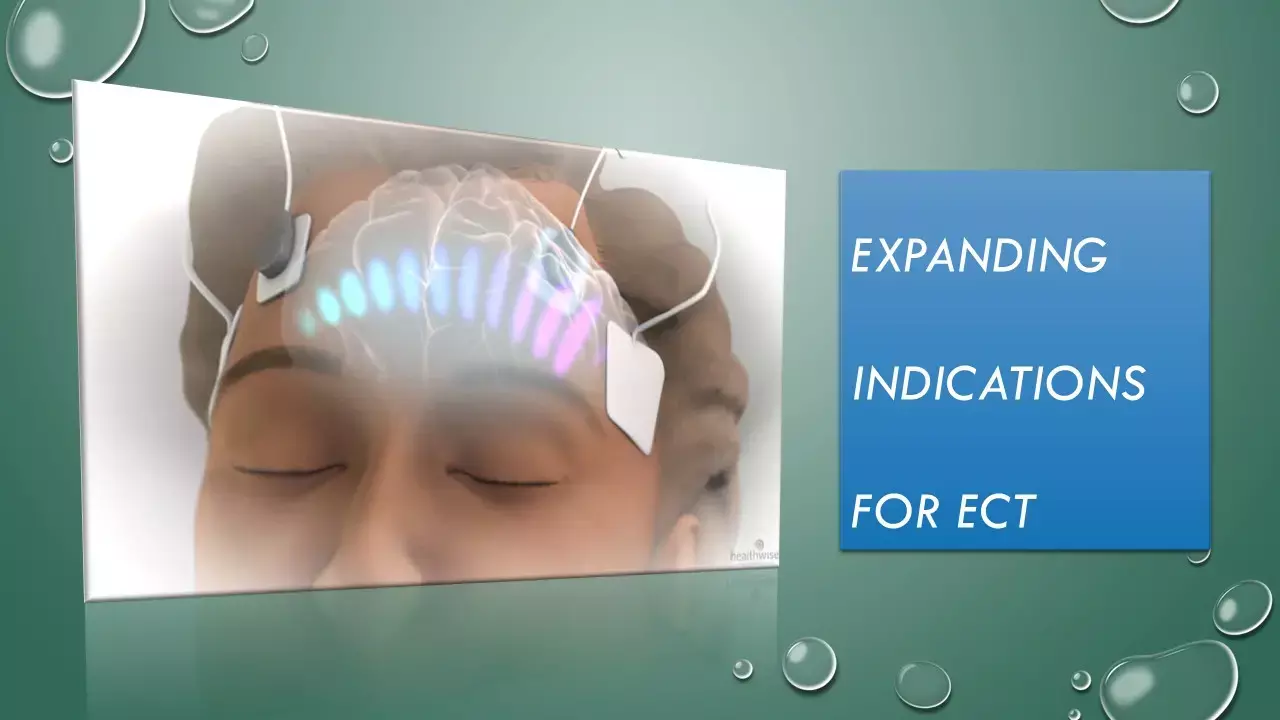
Neuropathic pain has high comorbidity rates for psychiatric disorders such as major depression or somatoform disorder. A case study published in Hindawi journal by Masashi Ueda et al, showed the efficacy of electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) in a patient having Neuropathic Pain, co-morbid with depression.
ECT is used in several psychiatric conditions such as major depression, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia. It has also been used for chronic pain with or without depressive symptoms. Deleterious changes in injured neurons associated with nociceptive receptors and descending modulatory pathways in the central nervous system can cause neuropathic pain.
The case represents a 41-year-old male whose right forearm was caught in a conveyor belt at a factory 2 years prior while at work, for which, he underwent a total of six surgeries on his right forearm, but he had residual numbness and pain in the first finger of his right hand and decreased grip strength in his right hand. The pain led to insomnia and depressive symptoms such as irritability and fatigue. The patient had not been prescribed any drugs for the pain. Paroxetine (37.5mg/day) and eszopiclone (2mg/day) were prescribed for his depressive state and insomnia. Nevertheless, the treatment did not improve the pain or the associated depressive state. ECT was tried for pain and depression. Eszopiclone was stopped 3 days before ECT but paroxetine was continued.
The Hamilton Rating Scale for depression (Ham-D) was 17 at this point. The patient's pain in the right forearm was rated a 10/10 on the Numeric Rating Scale (NRS), which was the most severe. A total of 12 sessions of bilateral ECT were performed using a Thymatron®.
The pain and depressive state gradually improved with the concomitant recovery of strength in the right hand with treatment. The Ham-D score was reduced to 6, and the NRS score decreased to 3 after the last ECT. After ECT, the patient was subsequently maintained with paroxetine (37.5mg/day), eszopiclone (2mg/day), and alprazolam (0.4mg/day), because the efficacy of ECT has been reported relatively transient. He has not yet experienced a relapse after one year since the last ECT.
ECT relieved the pain and subsequently lightened the motor restriction in his right forearm. ECT was effective in treating both neuropathic pain and depressive symptoms thus can be thought of as an alternative treatment for major depression associated with refractory neuropathic pain after traumatic injury.
Source: Hindawi journal: Ueda M, Konishi Y, Sakurai K, Ikenouchi A, Yoshimura R. Efficacy of Electroconvulsive Therapy for Neuropathic Pain Comorbid with Major Depression. Case Rep Psychiatry. 2020 Dec 5;2020:8818553. doi: 10.1155/2020/8818553.
M.B.B.S, M.D. Psychiatry
M.B.B.S, M.D. Psychiatry (Teerthanker Mahavir University, U.P.) Currently working as Senior Resident in Department of Psychiatry, Institute of Human Behaviour and Allied Sciences (IHBAS) Dilshad Garden, New Delhi. Actively involved in various research activities of the department.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


