- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Dietary Flavonoids may partially alleviate smoking-related COPD risk
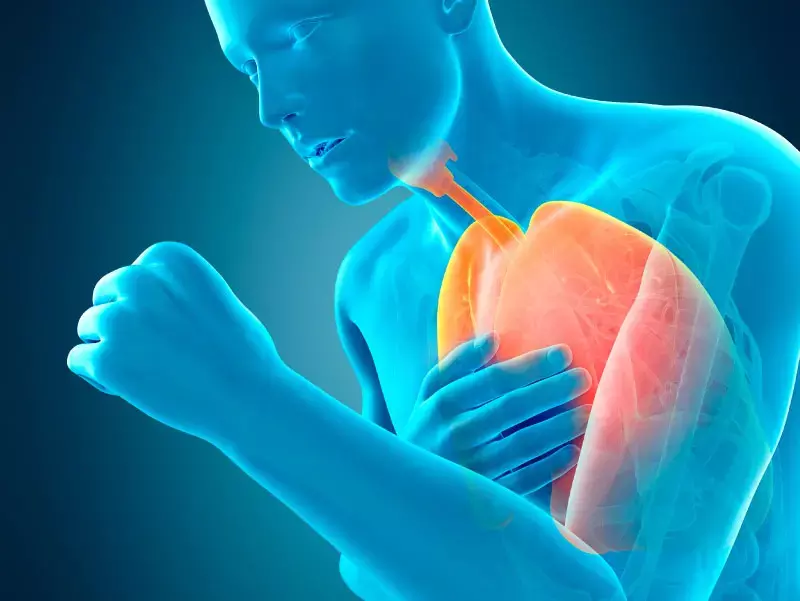
The risk of Smoking-related COPD can be partially mitigated by Dietary Flavonoids as found by a recent investigation. The study was published in the journal European Respiratory Journal.
Certain pulmonary function parameters can be benefitted by increasing flavonoid intake. But it is unknown if flavonoids have an effect on COPD too. Hence researchers conducted a study to examine associations between intakes of total flavonoids, flavonoid subclasses, and also major flavonoid compounds with incident COPD in participants from the Danish Diet, Cancer, and Health study.
The prospective cohort study included 55 413 men and women without COPD, aged 50–65 years at recruitment. A food frequency questionnaire using Phenol-Explorer was used to estimate the habitual Flavonoid intake. Incident cases of COPD were identified using Danish nationwide registers. Associations were modeled using restricted cubic splines within Cox proportional hazards models.
Results from the study:
- During 23 years of follow-up, 5557 participants were diagnosed with COPD.
- Of these, 4013 were current smokers, 1062 were former smokers and 482 were never-smokers.
- After multivariable adjustments, participants with the highest total flavonoid intakes had a 20% lower risk of COPD than those with the lowest intakes; a 6–22% lower risk was observed for each flavonoid subclass.
- The inverse association between total flavonoid intake and COPD was present in both men and women but only in current smokers and former smokers, not never-smokers.
- Furthermore, higher flavonoid intakes appeared to lessen, but not negate, the higher risk of COPD associated with smoking intensity.
Thus, the researchers concluded that Dietary flavonoids are important for partially mitigating the risk of smoking-related COPD. However, they suggested that smoking cessation should remain the highest priority.
To read more, click here: 10.1183/13993003.02604-2021
Bondonno NP, Parmenter BH, Dalgaard F, et al. Flavonoid intakes inversely associate with COPD in smokers. Eur Respir J. 2022;60(2):2102604. Published 2022 Aug 10.
BDS, MDS
Dr.Niharika Harsha B (BDS,MDS) completed her BDS from Govt Dental College, Hyderabad and MDS from Dr.NTR University of health sciences(Now Kaloji Rao University). She has 4 years of private dental practice and worked for 2 years as Consultant Oral Radiologist at a Dental Imaging Centre in Hyderabad. She worked as Research Assistant and scientific writer in the development of Oral Anti cancer screening device with her seniors. She has a deep intriguing wish in writing highly engaging, captivating and informative medical content for a wider audience. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751