- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Increasing salt intake linked to incident sleep apnea
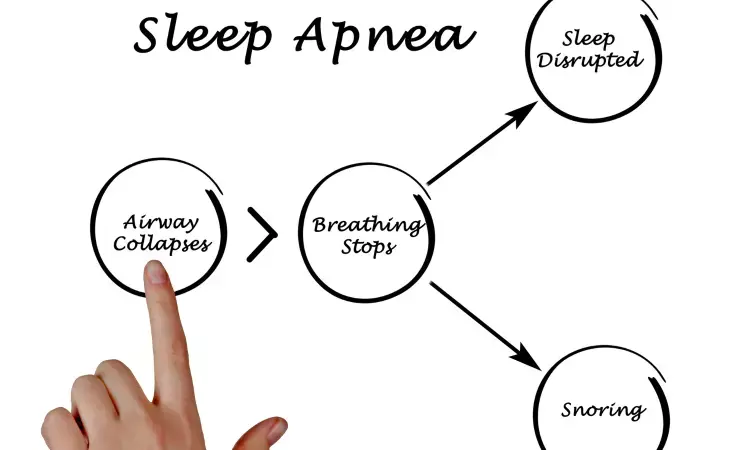
China: High salt intake may have an association with sleep apnea. According to a study published in Respiratory Research, researchers have said that adding salt to foods is independently tied to an increased risk of sleep apnea. The study has highlighted how beneficial salt reduction program is to prevent sleep apnea in the general population.
Sleep apnea affects 23% of women and 50% of men in the age group of 40–85 years. High sodium/salt intake contributes to the disease burden. It may have a role in pathogenesis through the mechanism of fluid retention. There needs to be data on whether adding salt to foods increases risk of sleep apnea.
Previous research mentioned that sodium-restricted diet intervention significantly decreases the frequency of apnea among such patients. Considering the above background, a study was conducted by a team of researchers led by Tingting Li from the Academy of Nutrition and Health at Wuhan University of Science and Technology to investigate this.
The study summary includes the following:
- The UK Biobank cohort study had more than 500,000 participants aged 40 to 69 years across the UK (2006-2010).
- A touch screen questionnaire was used to collect the frequency of adding salts to food.
- Cox proportional hazard regression model was used.
- There were 488,196 participants with a mean age of 56.5 years, and females were 55.0%.
- The follow-up was of 12.3 years.
- Six thousand three hundred ninety-four sleep apnea events occurred.
- Those who sometimes, usually, and always added salt to foods had an 11%, 15 % and 24 % higher risk of sleep apnea, having HR 1.11, 1.15 and 1.24, respectively.
To conclude, the habit of adding salt to foods causes a higher risk of incident sleep apnea.
Researchers said that a salt reduction program helps prevent sleep apnea.
The study's strength includes a large sample size, information, adjusting possible covariates, comprehensive sensitivity and subgroup analyses.
The limitations were challenges to distinguishing subtypes of sleep apnea, a single assessment of adding salt to foods at baseline; analyses was restricted to those participants with low OSA risk in the sensitivity analysis, and the reverse causality between the habit and incident sleep apnea cannot be eliminated.
Further reading:
Li, T., Song, L., Li, G. et al. Eating habit of adding salt to foods and incident sleep apnea: a prospective cohort study. Respir Res 24, 5 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-022-02300-6
BDS, MDS in Periodontics and Implantology
Dr. Aditi Yadav is a BDS, MDS in Periodontics and Implantology. She has a clinical experience of 5 years as a laser dental surgeon. She also has a Diploma in clinical research and pharmacovigilance and is a Certified data scientist. She is currently working as a content developer in e-health services. Dr. Yadav has a keen interest in Medical Journalism and is actively involved in Medical Research writing.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


