- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Nebulized normal saline improves respiratory symptoms in acute bronchiolitis: JAMA
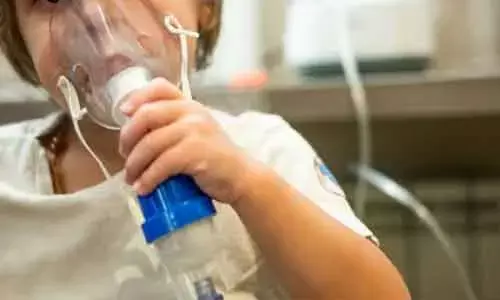
USA: Nebulized normal saline (NS) may be an active treatment for acute viral bronchiolitis, according to a recent review published in the journal JAMA Pediatrics. Nebulized NS is generally used as a placebo in clinical trials evaluating therapies for acute viral bronchiolitis.
In therapeutic trials for acute viral bronchiolitis, consistent clinical improvement in groups that received nebulized normal saline as placebo raised the question of whether nebulized NS acts as a treatment rather than a placebo.
Samantha A. House, Department of Pediatrics, Geisel School of Medicine, Dartmouth College, Hanover, New Hampshire, and colleagues undertook a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials in acute viral bronchiolitis using nebulized [normal saline] with 2 objectives: to compare nebulized [normal saline] with other forms of placebo (eg, non-nebulized placebo or sham nebulization) and to estimate the association of nebulized [normal saline] with short-term physiologic measures of respiratory status in randomized clinical trials in which it was used as the placebo.
The analysis included a total of 29 studies (n=1583).
Key findings of the study include:
- Standardized mean differences in respiratory scores for nebulized NS vs another placebo (3 studies) favoured nebulized NS by −0.9 points at 60 minutes after treatment.
- There were no differences in respiratory rate or oxygen saturation comparing nebulized NS with other placebo.
- The standardized mean difference in a respiratory score (25 studies) after nebulized NS was −0.7.
- The weighted mean difference in respiratory scores using a consistent scale (13 studies) after nebulized NS was −1.6 points.
- The weighted mean difference in respiratory rate (17 studies) after nebulized NS was −5.5 breaths per minute.
- The weighted mean difference in oxygen saturation (23 studies) after nebulized NS was −0.4%.
"Nebulized NS may be an active treatment for acute viral bronchiolitis. Further evaluation should occur to establish whether it is a true placebo," concluded the authors.
The study, "Evaluating the Placebo Status of Nebulized Normal Saline in Patients With Acute Viral Bronchiolitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis," is published in the journal JAMA Pediatrics.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


