- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Non-invasive ventilation improves outcomes in Respiratory failure due to Covid19: finds study
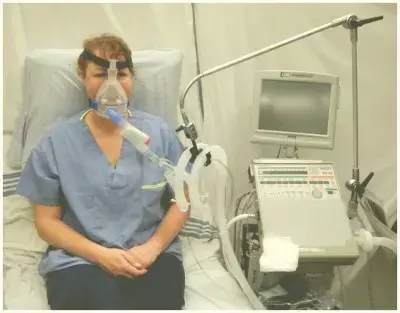
Acute hypoxic respiratory failure is one of the most common and dreadful complications of COVID-19 and is associated with poor outcomes. Evidence shows that use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) in case of acute hypoxic respiratory failure was known to improve arterial oxygenation, reduce work of breathing and recruit non-aerated alveoli in dependent pulmonary regions, thus reducing the need for endotracheal intubation (ETI).
Radovanovic et al conducted a review to study the outcome of patients treated with NIV/CPAP in Acute hypoxic respiratory failure secondary to Covid 19 pneumonia.
This rapid review included 23 manuscripts published since December-2019 until November-2020 with available data on in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients treated with NIV or CPAP. Most of the data was collected retrospectively and from single centre, while only 2 (9%) had a prospective observational design. A total of 4776 patients were included in the analysis.
The main findings of this rapid review can be summarized as follows:
1) The median positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP) used was on average 10 cmH2O.
2) Almost half of patients exposed to CPAP/NIV failed the non-invasive support trial and only half of cases were eligible for intubation
3) Overall in-hospital mortality was 40.9%
4) CPAP/NIV-related complications such as pneumothorax were uncommon
5) Length of hospital stay ranged from 6.2 days to 21 days
The indication for starting a noninvasive respiratory support in COVID-related ARDS is still debated. To date, oxygen supplementation to maintain SpO2 > 90% is strongly recommended but the utilization of NIV or CPAP is suggested with weak recommendation and very low quality of evidence. The main concerns being represented by the risk of aerosol generation and virus spread that could be harmful for the healthcare workers, and the ventilation-related lung injury secondary to late initiation of invasive mechanical ventilation. Indeed, guidelines suggest a careful titration of PEEP and low tidal volume ventilation due to the risk of barotrauma and volotrauma.
Authors conclude-"the application of non-invasive respiratory support with CPAP or NIV in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and acute hypoxic respiratory failure appears feasible and safe also outside the ICU setting".
Source: Radovanovic D, Coppola S, Franceschi E, Gervasoni F, Duscio E, Chiumello DA, Santus P. Mortality and clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia treated with non-invasive respiratory support: A rapid review. J Crit Care. 2021 May 21;65:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2021.05.007
MBBS, M. D. Respiratory Medicine
Dr Sravan Kumar V, completed his M. B. B. S from SRMC, Nandyal and M. D. in Respiratory Medicine from the JSS Medical College, Mysore. After completing MD. he worked as Senior resident in Kasturba Hospital, Manipal. He is actively involved in various research activities of the department. Currently he is working as senior resident in Mallareddy medical college for women, Hyderabad. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


