- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Researchers test BCG as a weapon against coronavirus
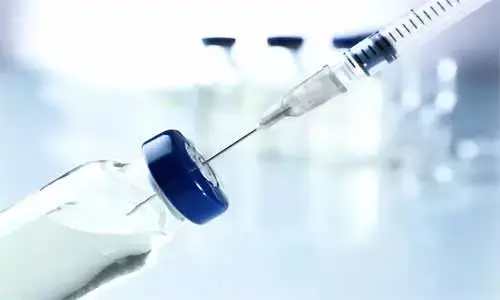
Australia:A vaccine that's been used to prevent tuberculosis is being given to health-care workers in Melbourne to see if it will protect them against the coronavirus.
The bacillus Calmette-Guerin, or BCG, shot has been used widely for about 100 years, with a growing appreciation for its off-target benefits. Not only is it a common immunotherapy for early-stage bladder cancer, it also seems to train the body's first line of immune defense to better fight infections.
With an immunization specifically targeted against the pandemic-causing Covid-19 disease at least a year away, the World Health Organization says it's important to know whether the BCG vaccine can reduce disease in those infected with the coronavirus, and is encouraging international groups to collaborate with a study led by Nigel Curtis, head of infectious diseases research, at the Murdoch Children's Research Institute in Melbourne.
"It can boost the immune system so that it defends better against a whole range of different infections, a whole range of different viruses and bacteria in a lot more generalized way," said Curtis, who's also a professor of pediatric infectious diseases at the University of Melbourne and head of the infectious diseases unit at the city's Royal Children's Hospital.
Hospital staff who volunteered to be part of a six-month trial in Australia involving 4,000 health-care workers will be randomly allocated to be vaccinated starting Monday against seasonal influenza and TB, or the flu shot only.
A placebo vaccine won't work as a control in this case because the BCG shot typically causes a localized skin reaction that leaves a scar, making it obvious which group received the TB vaccination.
Netherlands, Boston
Similar research is going on in the Netherlands. Curtis, in an interview Saturday, said he's in discussions with potential trial sites in other Australian cities as well as Boston.
Although the inexpensive vaccine, which is used to immunize some 130 million newborns worldwide each year, may potentially offer protection to a broader group of people, the priority is on health workers who are at higher risk from being infected with coronavirus while caring for sick patients.
"We need to think of every possible way that we can protect health-care workers," Curtis said. "And there's going to be a particular need to reduce the amount of time that our health-care workers are absent."
Studies in infants in Africa have shown that the BCG vaccine offers protection against TB and other pediatric infections, probably by enhancing the body's innate immune system -- specifically white blood cells that target non-specific pathogens before an antibody response has kicked in usually days later.
Blood samples taken at the start and end of the trial will determine who was infected with the coronavirus, while participants will log any symptoms during the trial period. The study's data monitoring committee will review the results after three months to look for any signs that the approach is working.
"We wouldn't be doing this if we didn't think that this might work," Curtis said. "We cannot guarantee that this will work. And of course, the only way to find out is with our trial."
Hina Zahid Joined Medical Dialogue in 2017 with a passion to work as a Reporter. She coordinates with various national and international journals and association and covers all the stories related to Medical guidelines, Medical Journals, rare medical surgeries as well as all the updates in the medical field. Email: editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


