- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Study Compares Clinical and Laboratory Aspects in COVID-19-Related and Non-COVID-19-Related ARDS Patients
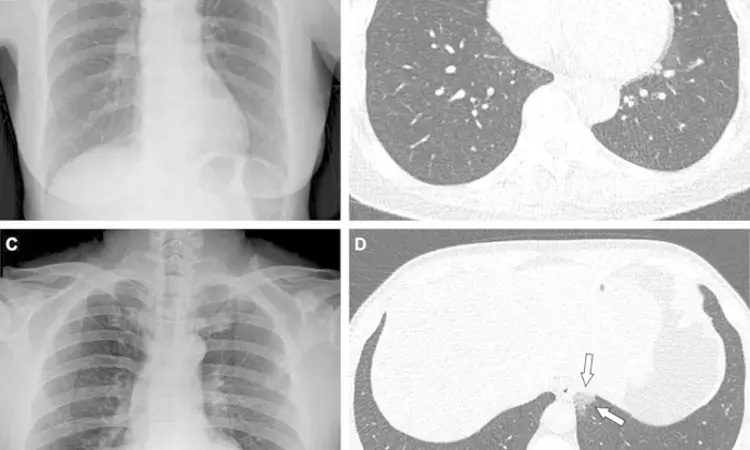
Representative cases showing pneumonia extents and patterns on chest X-ray (CXR) and CT images. (A and B) A 65-year-old female with breakthrough infection 2 months after a second dose of the Pfizer vaccine (fully vaccinated). The patient had a history of hypertension. (A) CXR obtained at admission showing no abnormal opacification in both lung zones. The CXR extent of pneumonia was scored as 0 (no evidence of pneumonia). (B) Axial chest CT image at the lower lobe level (obtained on the same day) showing negatively for pneumonia; CT extent of pneumonia was scored as 0 (no evidence of pneumonia). (C and D) A 48-year-old male with 1 month after a first dose of the AstraZeneca vaccine (partially vaccinated). The patient had no history of comorbidity. (C) CXR obtained at admission showing no abnormal opacification in both lung zones. The CXR extent of pneumonia was scored as 0 (no evidence of pneumonia). (D) Axial chest CT image obtained on the same day showing unilateral ground-glass opacity with a non-rounded morphology in the left lower lobe (arrows). CT extent of pneumonia was scored as 1 (1-25% involvement) and this case was classified as indeterminate appearance of COVID-19 according to the RSNA chest CT classification system.
CREDIT
Radiological Society of North America
The World Health Organization identified COVID-19 as a major global health threat. It predominantly impacts the respiratory system and can swiftly lead to ARDS, resulting in high ICU admission and mortality rates. Despite numerous studies on the clinical aspects of COVID-19, our comprehension of the disease is still limited. Recent study retrospectively compared the characteristics and treatment approaches of COVID-19-related acute respiratory distress syndrome (CARDS) patients and non-COVID-19-related ARDS (NCARDS) patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU). The study included 32 CARDS patients and 32 NCARDS patients.
The main findings from this research are:
This study highlights key similarities and differences in the clinical and laboratory characteristics as well as treatment approaches between CARDS and NCARDS patients. The authors conclude that CARDS and NCARDS have distinct features that should be considered in the management and follow-up of these patient populations. Understanding these differences is crucial for improving outcomes in ARDS patients.
The study faced certain limitations. Being retrospective, it relied on data from patient records and nurse observations. Additionally, due to missing arterial blood gas data, venous blood gas data were used. The study also lacked advanced ventilator data and had a small study population. Furthermore, the evolving nature of the COVID-19 pandemic and limited resources might have affected patient care and data availability.
Key Points -
The 3 key points of the research article are:
1. The study retrospectively compared the characteristics and treatment approaches of COVID-19-related acute respiratory distress syndrome (CARDS) patients and non-COVID-19-related ARDS (NCARDS) patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU). The study included 32 CARDS patients and 32 NCARDS patients.
2. The researchers found that CARDS and NCARDS have distinct clinical and laboratory characteristics, as well as different treatment approaches.
3. The authors conclude that the differences between CARDS and NCARDS should be considered in the management and follow-up of these patient populations, as understanding these differences is crucial for improving outcomes in ARDS patients.
Reference :
Yıldız N, Kaya E, Sahin A (July 04, 2024) A Retrospective Comparison of Clinical and Laboratory Aspects of Patients With COVID-19-Related
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) and Non-COVID-19-Related ARDS. Cureus 16(7): e63794. DOI 10.7759/cureus.63794
MBBS, MD (Anaesthesiology), FNB (Cardiac Anaesthesiology)
Dr Monish Raut is a practicing Cardiac Anesthesiologist. He completed his MBBS at Government Medical College, Nagpur, and pursued his MD in Anesthesiology at BJ Medical College, Pune. Further specializing in Cardiac Anesthesiology, Dr Raut earned his FNB in Cardiac Anesthesiology from Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, Delhi.


