- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Rare case of pulmonary edema reported with MRI contrast agent
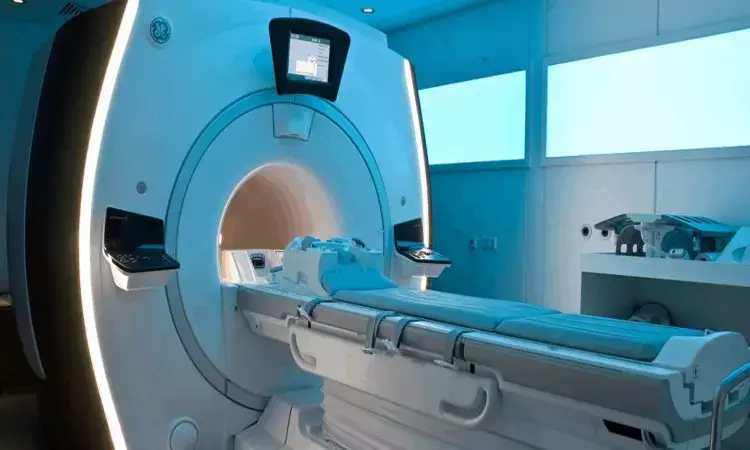
Turkey: A recent case study in the journal European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, describes the case of a patient who developed pulmonary edema from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agent.
Gadobutrol is a contrast agent often used during magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The agent has several side effects, some of which can be serious. It has extremely rare life-threatening systemic complications, which can lead to bronchospasm, hypersensitivity reactions, and cardiovascular arrest. However, there is no data available on the development of noncardiogenic pulmonary edema following the use of gadobutrol.
A. Demirhan, Department of Anesthesiology and Reanimation, Abant Izzet Baysal, University Medical School, Bolu, Turkey, and colleagues examined the case of a 37-year-old male patient who was reported to have developed noncardiogenic pulmonary edema after intravenous injection of gadobutrol during magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
According to the authors, this paper represents the first case of this complication.
In this case, rapid development of dyspnea and cyanosis immediately after administration of i.v. gadobutrol suggests NCPE (Noncardiogenic pulmonary edema). Rales were present in the lungs, the PaO2/FiO2 rate was less than 200, there was increased pulmonary vascular congestion on chest X-ray, and there was rapid response to treatment; all supporting NCPE. Gadobutrol associated skin lesions have rarely been reported. In our patient, excessive hypotension, despite the lack of skin lesions, suggests severe anaphylactic reaction. The patients' diagnosis was anaphylactic shock with noncardiogenic pulmonary edema and provides the first case in the current literature.
"Anaphylactic shock with noncardiogenic pulmonary edema after the use of gadobutrol is presented in this paper. As this is the first case in the literature, we suggest anaphylactic shock and noncardiogenic pulmonary edema must be kept in mind during MRI. Additionally, as in this case, accompanied hypopotassemia requires analysis and should be investigated in terms of gadobutrol attributable arrests, and, in particular, hERG mediated potassium current inhibition," concluded the authors.
"Magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent related pulmonary edema: a case report," is published in the journal European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


