- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
AI model accurately detects universal trauma on pelvic radiographs: Study
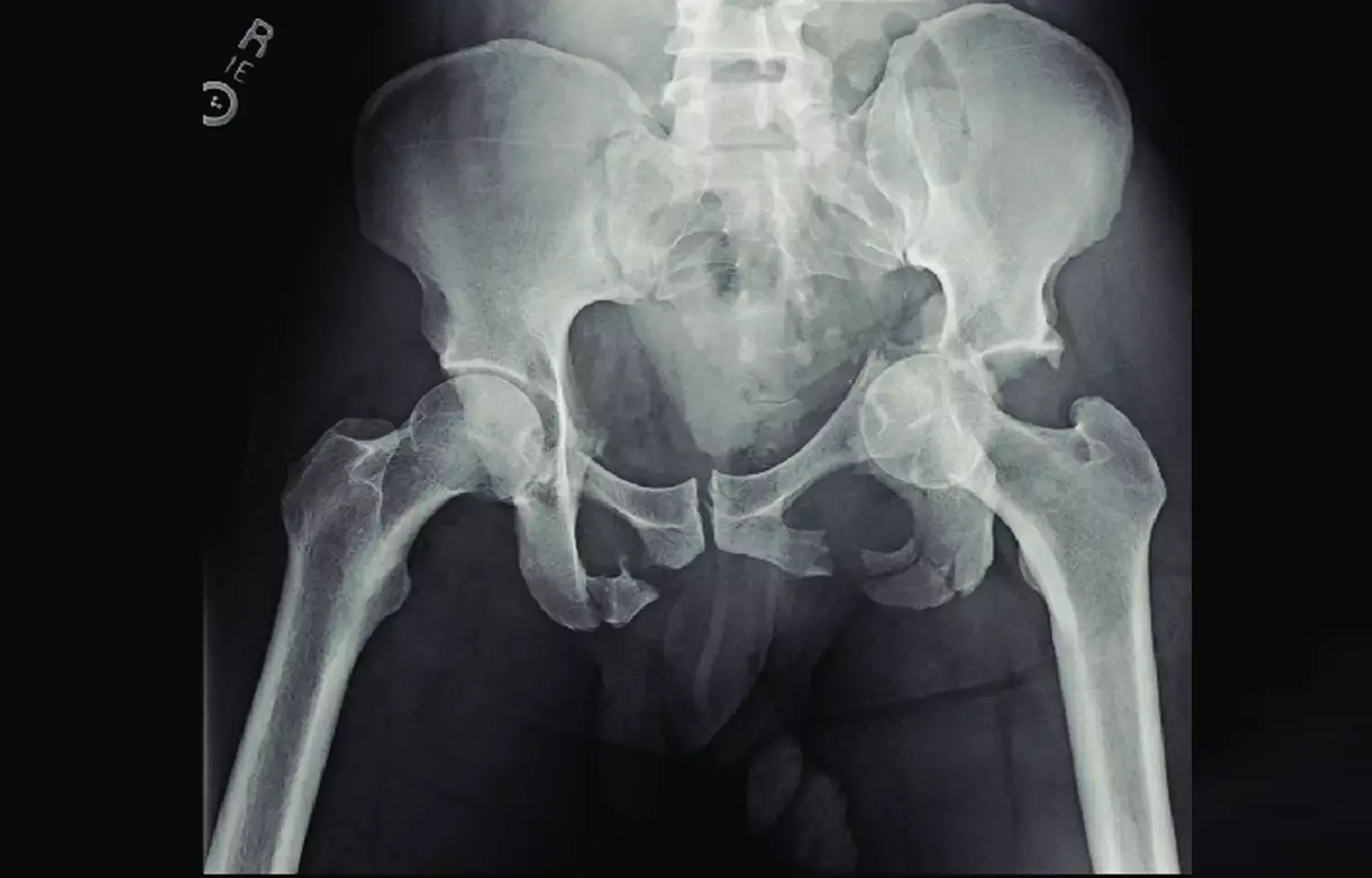
Taiwan: An artificial intelligence (AI) model can detect most types of trauma-related radiographic findings on pelvic radiographs (PXR), finds a recent study in the journal Nature Communications.
Pelvic radiograph is essential for the detection of proximal femur and pelvis injuries in trauma patients -- key component for trauma survey. None of the currently available algorithms are able to accurately detect all kinds of trauma-related radiographic findings on PXRs. Chien-Hung Liao, Chang Gung Memorial hospital, Linkou, Taoyuan, Taiwan, and colleagues developed a multiscale deep learning algorithm called PelviXNet trained with 5204 PXRs with weakly supervised point annotation.
Key findings of the study include:
- PelviXNet yields an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) of 0.973 and an area under the precision-recall curve (AUPRC) of 0.963 in the clinical population test set of 1888 PXRs.
- The accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity at the cutoff value are 0.924, 0.908, and 0.932, respectively.
- PelviXNet demonstrates comparable performance with radiologists and orthopedics in detecting pelvic and hip fractures.
"In this study, we developed an algorithm based on a point-supervised DL method that achieved high accuracy in identifying all kinds of trauma-related radiographic findings on PXRs. PelviXNet achieved an overall accuracy of 92.4% in a real-world population dataset," concluded the authors.
"Prospective studies are now required to determine if PelvixNet could lead to more precise diagnoses in a clinical environment and facilitate trauma patient management."
About Trauma Management
Trauma management is a race against time. A timely, accurate diagnosis with appropriate management is the key to saving lives. High-quality clinical trauma care and treatment not only rely on physician experience but also require information from various imaging modalities. Pelvic radiography is one of the diagnostic imaging modalities commonly used to evaluate blunt trauma patients. Pelvic radiographs (PXRs) cover the pelvis and the upper femur area, providing diagnostic value for orthopedic injuries in these regions, including hip fracture, pelvic fracture, hip dislocation, and other associated injuries.
The study titled, "A scalable physician-level deep learning algorithm detects universal trauma on pelvic radiographs," is published in the journal Nature Communications.
DOI: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-21311-3#Sec7
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


