- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
FAPI-SPECT Imaging: A Promising Tool for Predicting LV Remodeling After MI, study reveals
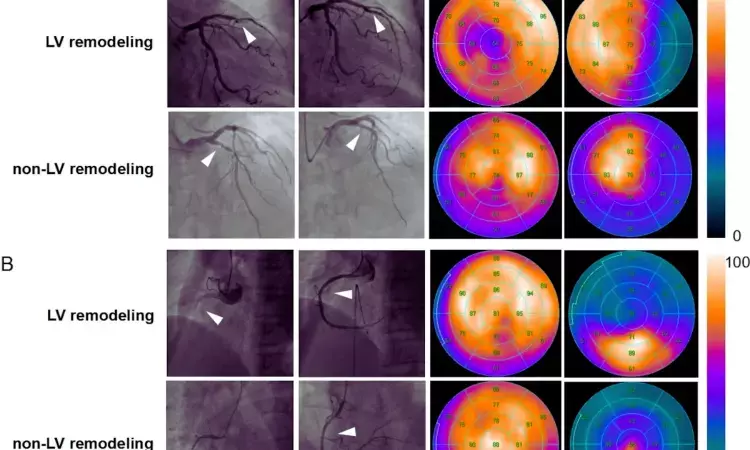
China: Technetium-99m (Tc-99m) fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (FAPI) single-photon emission CT (SPECT) has demonstrated potential for evaluating cellular and structural changes in the myocardium following a heart attack, a recent study has shown.
The researchers revealed that the novel method demonstrated abnormal cellular activity five days after a heart attack and detected so-called left ventricular (LV) remodeling after one year.
"The results of this study could transform post-acute myocardial infarction (MI) patient management by allowing for the early identification of individuals at risk for adverse left ventricular remodeling," Cuncun Hua, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China, and colleagues wrote in Journal of Nuclear Cardiology.
Left ventricular remodeling following a heart attack is a detrimental process characterized by cellular and structural changes in the myocardium, where the activation and proliferation of fibroblast cells play a crucial role. This remodeling can result in increased scar tissue formation in the heart, which is linked to the development of heart failure.
While PET imaging using F-18- and gallium-68 (Ga-68)-labeled fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (FAPI) radiotracers is well-established for assessing this activity, the authors noted that the use of Tc-99m FAPI-SPECT is gaining popularity due to its greater cost-effectiveness.
Against the above background, the researchers aimed to evaluate the predictive utility of 99mTc-radiolabeled fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (99mTc-HFAPi) single-photon emission computed tomography imaging in post-acute myocardial infarction (AMI) patients for evaluating 12-month left ventricular (LV) remodeling.
Fifty-eight patients with AMI (46 males, median age 61 [53, 67] years) underwent baseline 99mTc-HFAPi imaging (5 ± 2 days after MI), perfusion imaging (6 ± 2 days after MI), and echocardiography (2 ± 2 days after MI). Additionally, 15 patients received follow-up 99mTc-HFAPi and perfusion imaging, while 30 had follow-up echocardiography. Myocardial 99mTc-HFAPi activity was evaluated at the individual patient level. Left ventricular remodeling was defined as a ≥10% increase in left ventricular end-diastolic diameter (LVEDD) or left ventricular end-systolic diameter (LVESD) from baseline to follow-up echocardiography.
The study led to the following findings:
- AMI patients displayed localized but non-uniform 99mTc-HFAPi uptake, exceeding perfusion defects.
- Baseline 99mTc-HFAPi activity exhibited significant correlations with BNPmax, LDHmax, cTNImax, and WBCmax, inversely correlating with LVEF.
- After 12 months, 36.66% of patients experienced LV remodeling.
- Univariate regression analysis demonstrated an association between baseline 99mTc-HFAPi uptake extent and LV remodeling (OR= 2.14).
"99mTc-HFAPi SPECT imaging holds promise in predicting LV remodeling post-myocardial infarction, providing valuable insights for patient management and prognosis," the researchers wrote.
"This identification could lead to personalized interventions, potentially enhancing clinical outcomes and decreasing the risk of heart failure development," they concluded.
Reference:
Hua, C., Xi, X., Zhang, Y., Suo, N., Tu, B., Liu, Y., Yang, X., Liu, X., Su, P., Xie, B., Yang, M., & Wang, Y. (2024). 99mTc-HFAPi SPECT Imaging Predicts Left Ventricular Remodeling After Acute Myocardial Infarction. Journal of Nuclear Cardiology, 101910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nuclcard.2024.101910
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


