- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
NaF-PET/CT promising marker for disease severity and future risk in acute aortic syndrome patients: Study
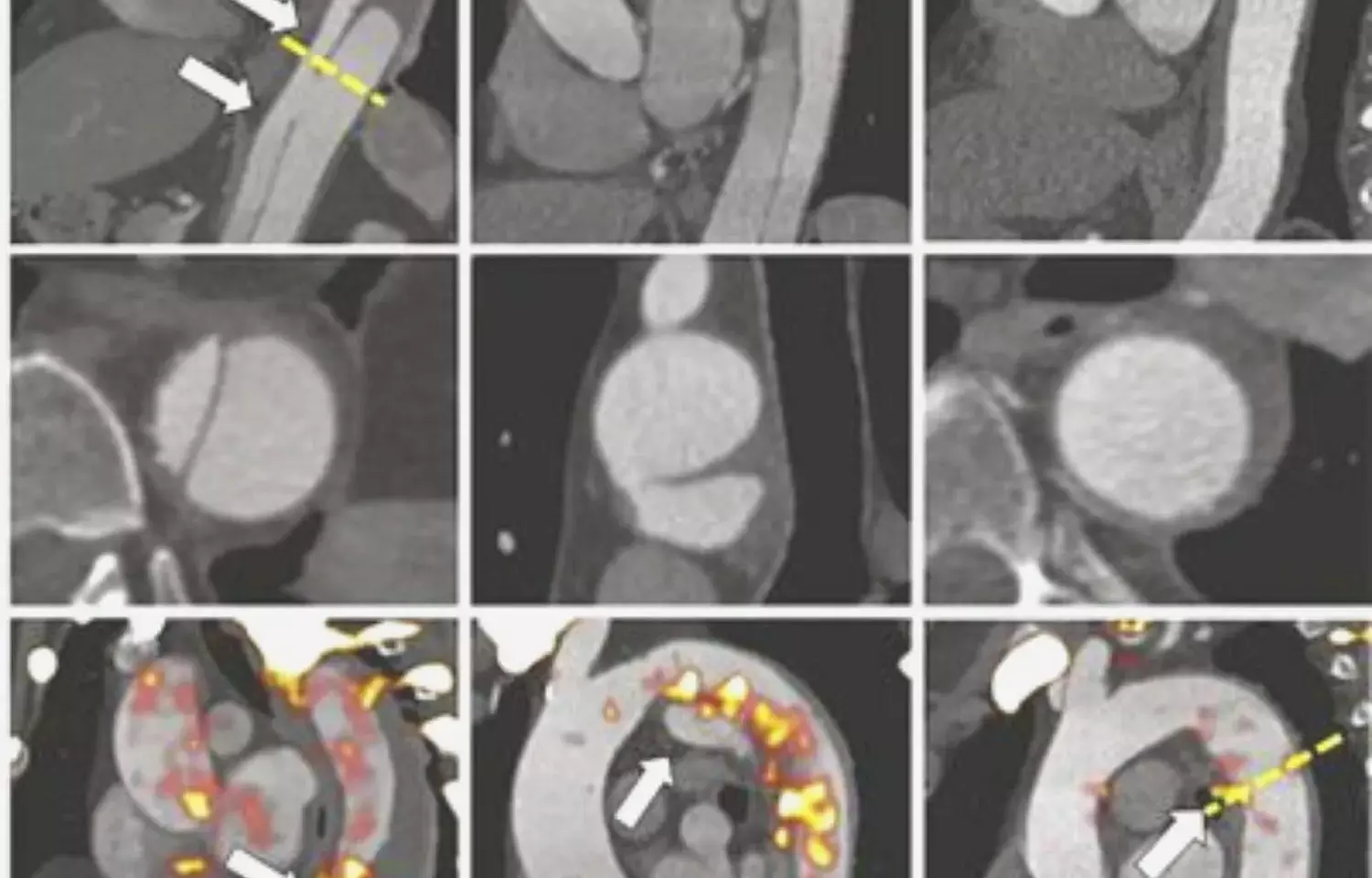
UK: PET-CT with F-18 sodium fluoride (NaF) is a promising noninvasive marker of disease severity and future risk in patients with acute aortic syndrome, suggests a recent study in the journal JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging. The study showed 18F-NaF uptake was enhanced at sites of disease activity and was linked with aortic growth and clinical events.
Acute aortic syndrome is linked with aortic medial degeneration. 18F-NaF PET can help in detecting microscopic tissue calcification as a marker of disease activity. Considering this, Maaz B.J.Syed, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, United Kingdom, and colleagues aimed to establish whether 18F-NaF positron emission tomography (PET) combined with computed tomography (CT) angiography could help in the identification of aortic medial disease activity in acute aortic syndrome patients.
For this purpose, the patients with aortic dissection or intramural hematomas and control subjects underwent 18F-NaF PET and CT angiography of the aorta. The measurement of aortic 18F-NaF uptake was done at the most diseased segment, and the maximum value was corrected for background blood pool activity (maximum tissue-to-background ratio [TBRmax]). The researchers then compared the uptake with the change in aortic size and major adverse aortic events (aortic rupture, aorta-related death, or aortic repair) over 45 ± 13 months.
Key findings include:
- Aortic 18F-NaF uptake co-localized with histologically defined regions of microcalcification and elastin disruption.
- Compared with control subjects, patients with acute aortic syndrome had increased 18F-NaF uptake (TBRmax: 1.36 ± 0.39 [n = 20] vs 2.02 ± 0.42 [n = 47] respectively) with enhanced uptake at the site of intimal disruption (+27.5%).
- 18F-NaF uptake in the false lumen was associated with aortic growth (+7.1 mm/year), and uptake in the outer aortic wall was associated with major adverse aortic events (HR: 8.5).
"18F-NaF uptake was enhanced at sites of disease activity in patients with acute aortic syndrome and was associated with aortic growth and clinical events," wrote the authors. "18F-NaF PET-CT holds promise as a noninvasive marker of disease severity and future risk in patients with acute aortic syndrome."
Reference:
The study titled, "18F-Sodium Fluoride Positron Emission Tomography and Computed Tomography in Acute Aortic Syndrome," was published in the journal JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmg.2022.01.003
KEYWORDS: JACC, acute aortic syndrome, PET, CT, sodium fluoride, imaging, aortic wall, Maaz B J Syed, computed tomography, positron emission tomography, cardiovascular imaging, aorta
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


