- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Novel Imaging Method Locates Cardiac Arrhythmias, Finds Study
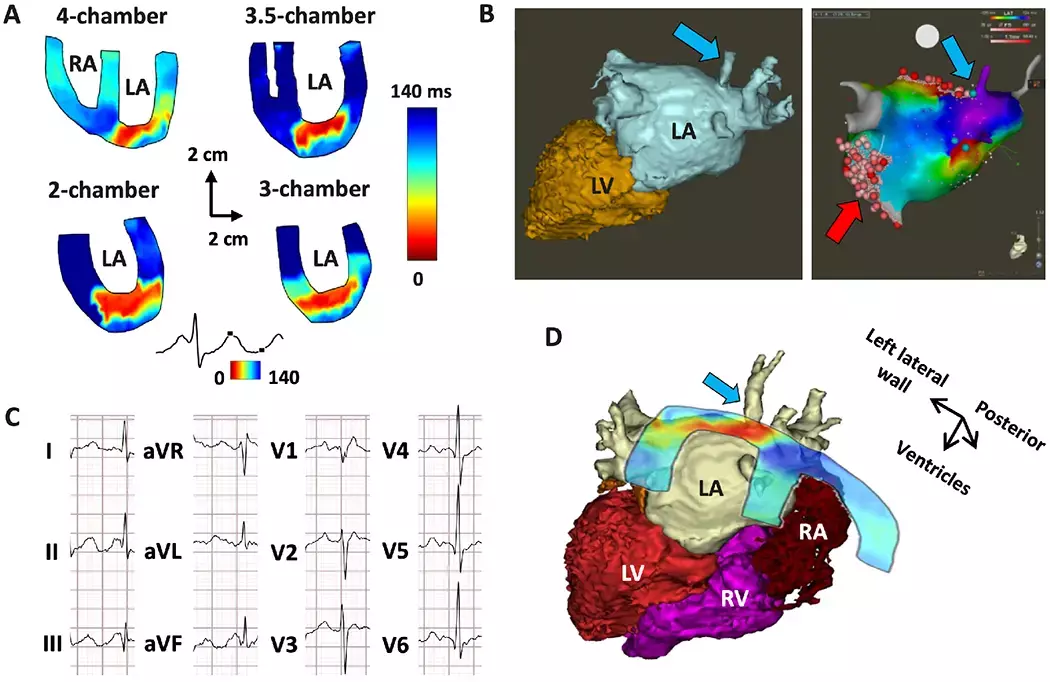
Courtesy PubMed, EWI isochrones of a left atrial roof tachycardia
Cardiac arrhythmias are a cause of morbidity and mortality, often necessitating invasive catheter ablation for curative treatment. Diagnosis and localization of cardiac arrhythmias are critical for clinical decision making and treatment planning. In a study, researchers have used noninvasive ultrasound called electromechanical wave imaging (EWI) to generate maps of the heart and to identify the sites of arrhythmias suggesting that the addition of this imaging method to clinical workflows could help improve decision-making and treatment planning. The research has been published in the journal Science Translational Medicine on March 25, 2020.
Electrocardiogram (ECG) algorithms have been proposed to aid in the localization of arrhythmias but have varying accuracy, and inter-observer variability is common. EWI is a high frame rate ultrasound technique that can noninvasively map with high accuracy the electromechanical activation of atrial and ventricular arrhythmias in adult patients. There has been some controversy regarding the accuracy of the inverse solution in ECGI (electrocardiogram imaging). Exploration of other noninvasive mapping approaches, such as EWI, is therefore warranted. Dr Christopher S. Grubb and his team conducted a study to evaluate the accuracy of EWI for localization of various arrhythmias in all four chambers of the heart before catheter ablation.
Researchers included a total of fifty-five patients with an accessory pathway (AP) with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW), premature ventricular complexes (PVC), atrial tachycardia (AT), or atrial flutter (AFL) underwent transthoracic EWI and 12-lead ECG. They compared the diagnostic accuracy of both atrial and ventricular EWI isochrones (multi-2D or 3D-rendered) with 12-lead ECG-based localization by expert electrophysiologists and finally to the gold standard of 3D electroanatomical maps performed with invasive catheter mapping and eventual successful site of ablation.
Key findings of the study were:
- Upon evaluation, the researchers found significant inter-observer variability amongst 12-lead ECG reads by expert electrophysiologists.
- They also found that EWI correctly predicted 96% of arrhythmia locations as compared with 71% for 12-lead ECG analyses [unadjusted for arrhythmia type: odds ratio (OR): 11.8; adjusted for arrhythmia type: OR: 12.1].
The authors concluded, "This double-blinded clinical study demonstrates that EWI can localize atrial and ventricular arrhythmias including WPW, PVC, AT, and AFL. EWI when used with ECG may allow for improved treatment for patients with arrhythmias."
For further information:
https://stm.sciencemag.org/content/12/536/eaax6111
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


