- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Photon-Counting Detector CT Promising Alternative for Liver Fat Quantification in MASLD, shows research
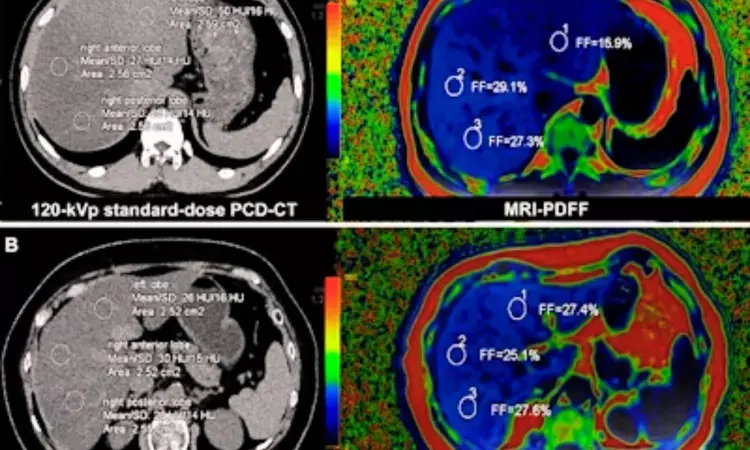
China: A recent study published in the Radiology Journal has shown that photon-counting CT could be a viable alternative to MRI for evaluating liver fat in patients with fatty liver disease. A team of researchers from China conducted a clinical trial involving a large group of patients and discovered that the technique performed comparably to MRI proton density fat fraction, which is currently the most accurate method for assessment.
The team stated, "This study confirmed that photon-counting detector CT can provide accurate, protocol-independent liver fat quantification in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease across different imaging environments."
The authors emphasized that accurately quantifying liver fat is crucial for the treatment and monitoring of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), which affects up to 24% of the U.S. population and can progress to cirrhosis or cancer if untreated. While MRI is a well-established noninvasive method for assessing liver fat, it requires patients to hold their breath for 20 seconds during image acquisition, which can compromise image quality. Additionally, MRI may not be feasible for patients with metal implants or those who are claustrophobic.
In contrast, photon-counting CT offers several advantages, such as improved spatial resolution and spectral separation, and early studies suggest it may effectively quantify liver fat, even in obese patients. However, further robust studies are necessary to validate this technology.
Against the above background, Huimin Lin, From the Department of Radiology, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China, and colleagues developed and validated a universal CT to MRI fat conversion formula to enhance fat quantification accuracy across several PCD CT protocols compared to MRI proton density fat fraction (PDFF).
For this purpose, the researchers evaluated how well fat can be measured using different fat levels in phantoms. They enrolled 500 healthy participants and 157 with suspected metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) between September 2023 and March 2024. Participants were randomly divided into six groups based on different CT settings for tube voltage (90, 120, or 140 kVp) and radiation dose (standard or low).
In the group with 120 kVp and standard dose, 51% (53 out of 104) were used to train the model, while the rest served as a validation group. A formula to estimate the CT-derived fat fraction (CTFF) from MRI was created using the training group. The researchers then compared how closely the CTFF matched with MRI results in the validation group and looked at variations based on tube voltage, radiation dose, body mass index, and in the MASLD group. They also examined the factors affecting the CTFF's accuracy.
The study led to the following findings:
- In the phantoms, CTFF showed excellent agreement with a nominal fat fraction (intraclass correlation coefficient, 0.98; mean bias, 0.2%).
- The trial included 412 asymptomatic participants and 122 participants with MASLD.
- A CT to MRI fat conversion formula was derived as follows: MRI PDFF (%) = −0.58 · CT (HU) + 43.1.
- Across all comparisons, CTFF demonstrated excellent agreement with PDFF (mean bias values < 1%).
- CTFF error was not influenced by tube voltage, radiation dose, body mass index, or PDFF.
- Agreement between CTFF and PDFF was also found in the MASLD cohort (mean bias, −0.2%).
"The standardized CT value from photon-counting CT demonstrated strong and consistent agreement with MRI proton density fat fraction across different protocols, suggesting it could be a reliable alternative for measuring liver fat," the researchers concluded.
Reference:
DOI: https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/10.1148/radiol.240038
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


