- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
POCUS effective for localizing PICCs in neonate patients: Study
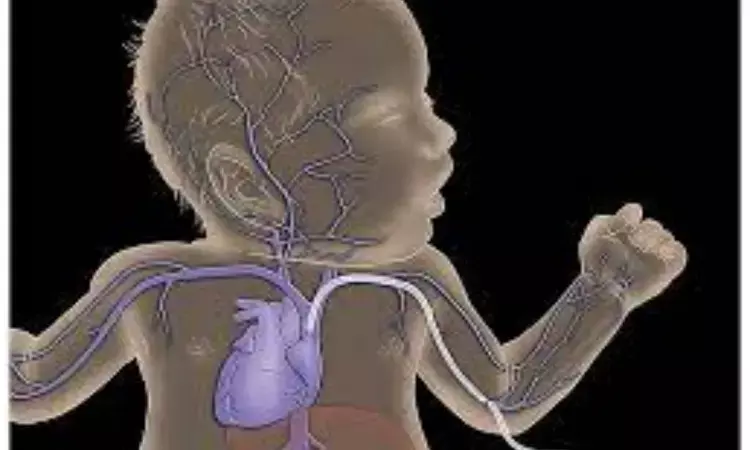
Naples, Italy: A recent study has found point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) to be an effective and non-invasive alternative to the conventional radiogram for localizing small-bore percutaneously inserted central catheters (PICC) in newborns. The researchers in their study, published in the Journal of Pediatrics, suggest that the conventional radiogram should be recommended when ultrasound fails to locate catheter tip.
For critically ill newborn patients, a central venous catheter may be needed for drug administration and nutrition. Typically, a PICC, made up of small-bore silicone or polyurethane device, is used. It is inserted through the superficial veins of the limbs, the neck, or the scalp. A radiograph is a common imaging method used to assess the catheter tip location. However, its use is limited by the fact that it uses ionizing radiation.
Previous studies have shown ultrasound to be a good alternative to radiographs as it is radiation-free and is a repeatable bedside option for experienced clinicians. Also, POCUS is being touted by researchers owing to its s portability and cost-effectiveness, while having accuracy comparable with that of standard ultrasound.
Against the above background, Fiorentino Grasso, Section of Neonatology, Department of Translational Medical Sciences, Federico II University, Naples, Italy, and colleagues in their study aimed to assess POCUS guided catheter tip location in a neonatal cohort following insertion of PICCs from the upper part of the body.
The research was designed as a prospective, observational study on PICC tip location. The tip site was assessed by radiological landmarks or direct ultrasound (US) visualization of the cardiovascular structures.
Following were the study's key findings:
· One-hundred eighteen PICCs (28 G/1 Fr) were studied in 102 neonates (mean postmenstrual age: 31 weeks; mean weight at positioning: 1365 grams).
· Feasibility of POCUS guided tip location was 92.3% in our population. Failures were significantly associated with mechanical ventilation (aOR 5.33).
· Agreement between US and radiographic methods was found in 88 out of 109 cases (80.7%).
· Fifteen out of 21 discordant cases led to a change in clinical management.
"Our findings showed that POCUS guided localization of small bore PICC is a non-invasive and effective alternative to the conventional radiogram, the authors concluded". "The latter should be recommended when US fails to locate the catheter tip."
Reference:
The study titled, "Ultrasound guided catheter tip location in neonates: a prospective cohort study," was published in the Journal of Pediatrics.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


