- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Repeat CT must in Coronavirus patients with negative CT but worsening symptoms: Study
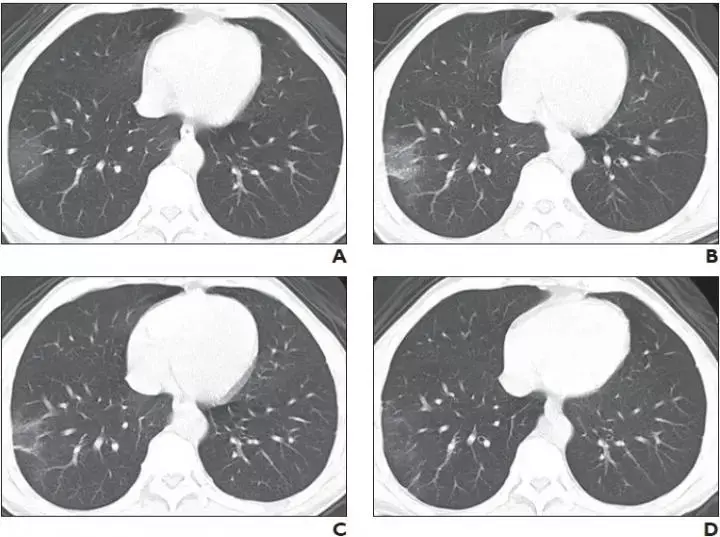 CT scoring criteria were applied to images from sequential chest CT examinations. A, Initial chest CT image obtained 2 days after onset of symptoms shows small region of subpleural ground-glass opacities in right lower lobe, for CT score of 1. B, Chest CT image obtained on day 3 of treatment shows slightly enlarged region of subpleural ground-glass opacities with partial crazy-paving pattern and consolidation, for CT score of 3. C, Chest CT image obtained on day 5 of treatment shows partial resolution of co
CT scoring criteria were applied to images from sequential chest CT examinations. A, Initial chest CT image obtained 2 days after onset of symptoms shows small region of subpleural ground-glass opacities in right lower lobe, for CT score of 1. B, Chest CT image obtained on day 3 of treatment shows slightly enlarged region of subpleural ground-glass opacities with partial crazy-paving pattern and consolidation, for CT score of 3. C, Chest CT image obtained on day 5 of treatment shows partial resolution of coResearchers have found that In COVID-19 patients with negative initial chest CT findings, repeat CT is necessary for monitoring the disease, especially when patients have worsening symptoms or laboratory indicators.
The study by Binjie Fu and colleagues in Department of Radiology, Yongchuan Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, China has reported development of new pulmonary lesions in COVID-19 patients with negative initial chest CT findings.
The findings of the study have been published in journal of Infection and Drug Resistance.
The epidemic of COVID-19 has attracted much attention because of its sudden progression from being asymptomatic to severe and life threatening pulmonary involvement. Thus, CT has emerged to be a common method for COVID-19 diagnosis, as it can quickly and efficiently provide information about pulmonary lesions.
The study aimed at reviewing the follow-up CT of COVID-19 patients with negative initial chest CT findings while evaluating changes in clinical manifestations and laboratory indicators of patients with newly developed lesions and studying the correlation of clinical and laboratory data with imaging results.
Researchers collected data retrospectively from 29 patients who had tested positive for COVID-19 by reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction testing but negative by initial chest CT from January 22 to February 17, 2020. Clinical manifestations, laboratory indicators, and follow-up CT data were further evaluated. Mean time from onset of new lesions to initial CT was 5.8 ± 3.0 days (range: 2– 12 days).repeat CT was done and assessed for any new lesions.
Findings revealed the following key facts-
- New pulmonary lesions developed in 10 (34.5%) patients on follow-up CT.
- New lesions (mean involved lobes and segments: 2.5 ± 1.6 [range: 1– 5] and 4.5 ± 4.5 [range: 1– 13]) were mainly spherical/patchy ground-glass opacities frequently located in the left lower lobe (9, 90.0%).
- Among the 10 patients, lesions in 6 (60.0%) indicated progression after occurrence.
- When new lesions developed, 6 (60.0%) patients developed new symptoms or had aggravated symptoms and 3 (30.0%) had decreased lymphocyte count.
- Patients with worsening symptoms had higher involvement of lung segments (mean: 6.5 ± 5.0, range: 1– 13) than asymptomatic patients (mean: 1.5 ± 0.6, range: 1– 2) .
Authors wrote that even if initial chest CT findings were negative in COVID 19 patients, new pulmonary lesions may develop during treatment. In addition, changes in clinical symptoms may be related to the extent of pulmonary involvement since patients with aggravated or new symptoms typically had relatively more involved lung segments than asymptomatic cases. The newly developed lesions may be localized or extensive, and most will temporarily progress but significantly be absorbed subsequently.
They recommended repeat CT for monitoring the disease, especially when patients have worsening symptoms or laboratory indicators.
Researchers concluded that the relatively small sample size makes it necessary to assess the follow up CT findings of COVID 19 patients with similar initial radiological findings in a larger population.
Dr Satabdi Saha (BDS, MDS) is a practicing pediatric dentist with a keen interest in new medical researches and updates. She has completed her BDS from North Bengal Dental College ,Darjeeling. Then she went on to secure an ALL INDIA NEET PG rank and completed her MDS from the first dental college in the country – Dr R. Ahmed Dental College and Hospital. She is currently attached to The Marwari Relief Society Hospital as a consultant along with private practice of 2 years. She has published scientific papers in national and international journals. Her strong passion of sharing knowledge with the medical fraternity has motivated her to be a part of Medical Dialogues.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


