- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Bile duct injury rates higher from robotic assisted cholecystectomy, suggests study
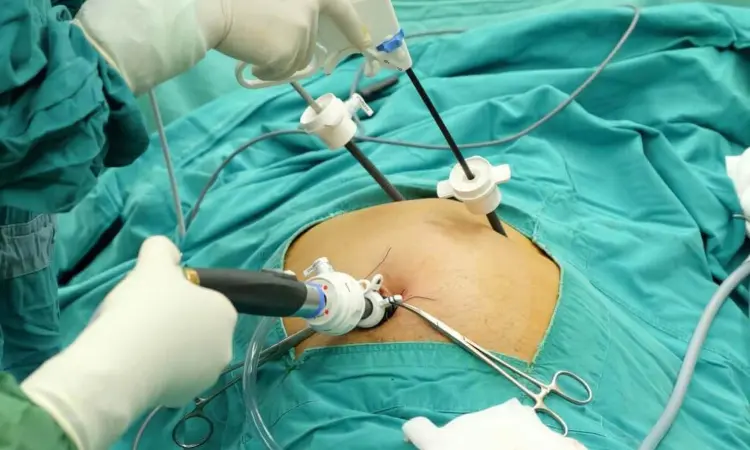
As robotic cholecystectomy, also known as gallbladder removal, becomes increasingly common, researchers have identified higher rates of bile duct injury in robotic cholecystectomy compared to the conventional approach, a laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
A team of researchers at University of Michigan Health led by Cody Mullens, M.D., M.P.H., a general surgery resident, found that there are higher risks of bile duct injury in robotic cholecystectomy, regardless of patient risk factors.
Bile duct injuries are rare and a technical complication from a cholecystectomy but should be treated quickly once located.
An injured bile duct can result in a flow of bile from the liver into the gastrointestinal tract that assists in digestion and absorption which can proceed to leak out into the abdomen.
This can result in further procedures being needed to repair the injured bile duct and stop the leakage.
The purpose of the study was to challenge the claim by surgeons that differences in bile duct injury rates in robotic versus laparoscopic cholecystectomy was due to patient-selection factors.
Using Medicare data, Mullens and team were able to determine that bile duct injury is higher in robotic cholecystectomy compared to laparoscopic cholecystectomy in low, medium, and high risk patients.
“Given these findings and other recent work, patients should be having honest conversations with their surgeons about the risk of using the robotic vs. laparoscopic techniques for a cholecystectomy,” said Mullens.
“While most outcomes are similar between robotic and laparoscopic gallbladder removal, this evidence clarifies that patient risk factors should not be driving decision-making about whether the gallbladder should be removed robotically or laparoscopically.”
Mullens also pointed out that across the different levels of patient risk, bile duct injury was approximately three times higher for robotic cholecystectomies than laparoscopic.
“Across the board, patients are having less bile duct injuries with laparoscopic cholecystectomies than robotic assisted.”
Reference:
Mullens CL, Sheskey S, Thumma JR, Dimick JB, Norton EC, Sheetz KH. Patient Complexity and Bile Duct Injury After Robotic-Assisted vs Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy. JAMA Netw Open. 2025;8(3):e251705. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.1705
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


