- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Gastrojejunostomy and endoscopic stenting effective for Gastric outlet obstruction: Study
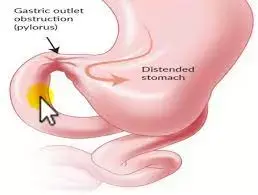
Both Gastrojejunostomy (GJ) and endoscopic stenting (ES) are safe and effective intervention modalities for malignant Gastric outlet obstruction (GOO), according to a recent study published in the American Journal of Surgery.
Gastric outlet obstruction (GOO) is a recognized common complication in patients with upper gastrointestinal cancer. The incidence of pancreatic cancer is 7.1 cases per 100,000 people, and about 15–20% of these patients develop GOO.2 In addition, GOO is also one of the typical clinical symptoms of advanced gastric cancer. GOO is typically accompanied by severe nausea, vomiting, bloating, and malnutrition, significantly impacting patients' survival and quality of life.3 Since most patients suffer from locally advanced or metastatic cancers and have a poor prognosis, the main objectives of palliative treatment are to improve the general condition of patients, re-establish an oral intake quickly, with minimal complications, and without compromising survival.
This study aimed to determine the optimal intervention modality for malignant GOO by comparing clinical outcomes after Gastrojejunostomy and endoscopic stenting. Two authors independently searched Web of Science, PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library for articles before February 2021 to compare the clinical outcomes of GOO patients undergoing GJ or ES.
The Results of the study are as follows:
This meta-analysis included 31 articles with 2444 GOO patients. Although the GJ group outperformed the ES group in technical success (OR,3.79; P = 0.003), clinical success was not significantly different between the two groups (OR,1.25; P = 0.50). The GJ group had a longer hospitalization, lower re-obstruction and lower reintervention. Moreover, GJ had better survival than ES in the gastric cancer group (HR, 0.33; P = 0.009). However, no significant statistical difference was observed in the pancreatic cancer group (HR, 0.55; P = 0.159).
Thus, the researchers concluded that both GJ and ES are safe and effective intervention modalities for malignant GOO. GJ had significantly improved survival in gastric cancer patients with GOO, while no significant difference was observed between the two groups in pancreatic cancer patients with GOO.
Reference:
Comparison of gastrojejunostomy to endoscopic stenting for gastric outlet obstruction: An updated Systematic Review and Meta‐analysis Jiaze Hong et al published in the American Journal of Surgery.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2021.10.038
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


