- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Laparoscopic appendectomy safer than open surgery for patients of acute appendicitis
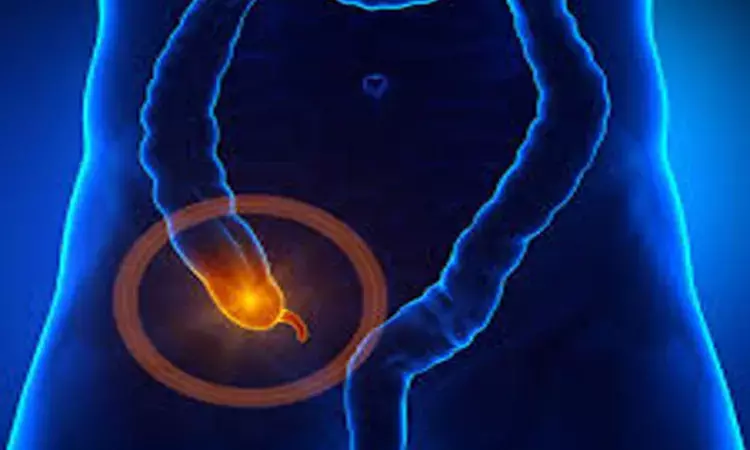
China: Laparoscopic appendectomy (LA) is a safe and feasible procedure for the treatment of patients with acute appendicitis (AA), a recent study in the World Journal of Emergency Surgery has stated.
The meta-analysis found that laparoscopic appendectomy compared to open appendectomy (OA) was advantageous in terms of fewer adverse reactions, fewer complications, shorter operation time and hospitalization, and lower inflammatory response.
Guangzhe Zhang & Bo Wu from The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning, China compared the postoperative recovery of patients with acute appendicitis after laparoscopic appendectomy and open appendectomy and aimed to determine the optimal diagnosis and treatment plan for appendectomy.
For this purpose, the researchers searched the online databases for the related literature. To extract data, articles on LA and OA for AA published between 2010 and 2021 were selected. Stata16.0 was used for meta-analysis.
Based on the study, the researchers reported the following findings:
· A total of 777 articles were retrieved, and 16 of them were finally selected. Totally, 1251 patients underwent LA, while 898 patients received OA.
· According to the results of the meta-analysis, LA was associated with a lower incidence of adverse reactions [OR = 0.257], shorter operation time (SMD = − 1.802), and hospitalization (SMD = − 1.184).
· In addition, compared with the OA group, LA was found with less intraoperative blood loss (SMD = − 3.650) and shorter recovery time of gastrointestinal function (SMD = − 3.010).
· Aside from all these, the counts of leukocyte (SMD = − 0.432), neutrophil (SMD = − 1.346), and C-reactive protein (SMD = − 2.391) all decreased in a significant manner after LA.
"LA is advantageous in terms of having shorter operation times and hospital stays, fewer adverse reactions, lower inflammatory response, and fewer complications. Hence, it is safe and feasible surgery for AA," the authors wrote in their study.
"The study serves to fill the knowledge gap in the literature discussing the optimization of postoperative recovery by LA, and lays a solid theoretical basis for the development of clinical diagnosis and treatment plan for AA," they concluded.
Reference:
Zhang, G., Wu, B. Meta-analysis of the clinical efficacy of laparoscopic appendectomy in the treatment of acute appendicitis. World J Emerg Surg 17, 26 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13017-022-00431-1
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


