- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Reduced port laparoscopic posterior mesh rectopexy effective surgery option for full-thickness rectal prolapse: Study
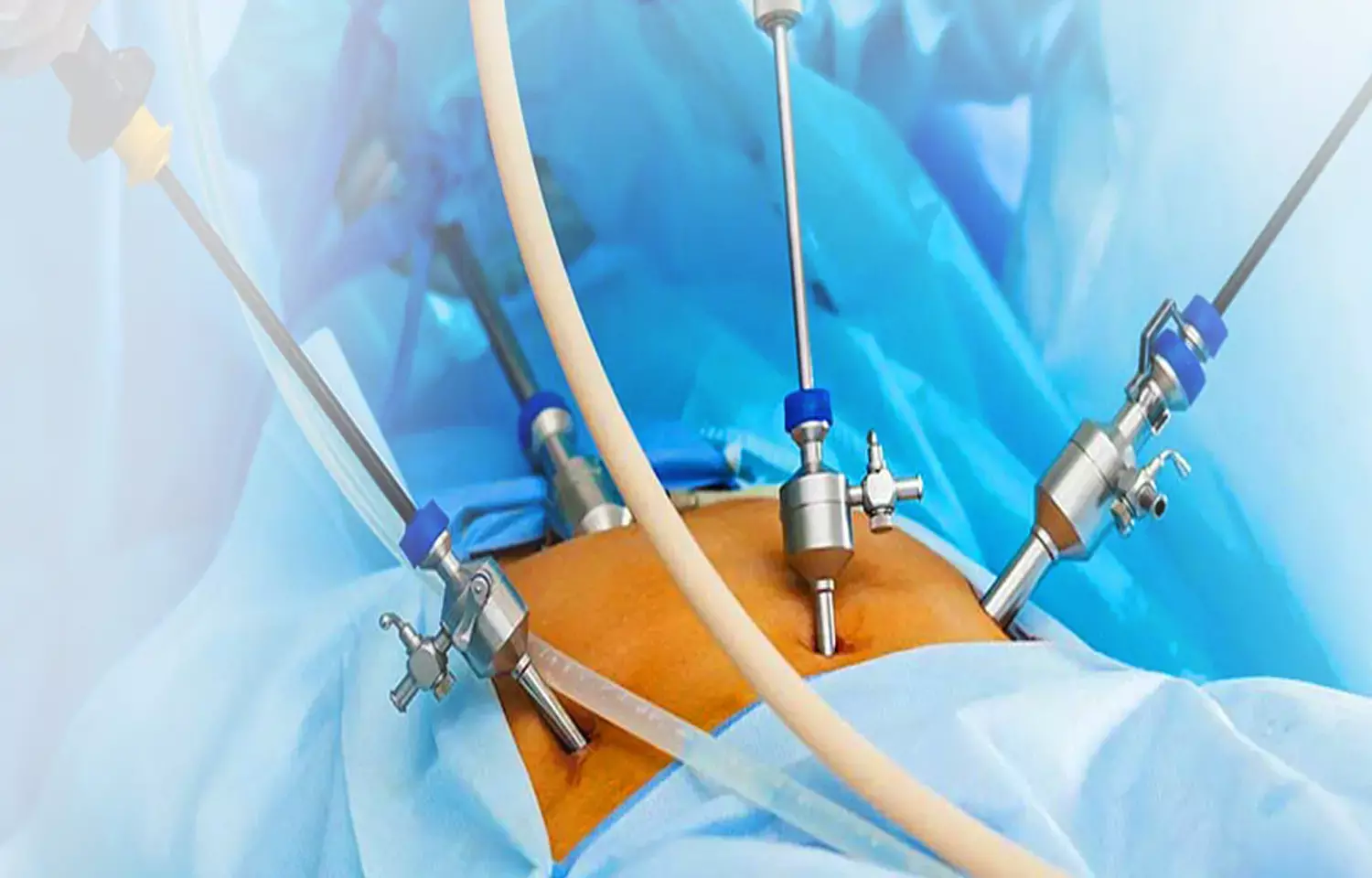
A recent study found that Reduced port laparoscopic posterior mesh rectopexy may serve as an effective therapeutic option for full-thickness rectal prolapse. Compared to the conventional multiport surgery (MPS), reduced port surgery was found to have smaller wound sizes and better cosmetic outcomes. The study results were published in the journal BMC Surgery.
Laparoscopic rectopexy has long been considered a reliable treatment for full-thickness rectal prolapse. More recently, reduced port surgery (RPS) has gained attention as a new approach that potentially offers benefits over the traditional multiport surgery (MPS) technique. The primary advantages proposed for RPS include reduced postoperative pain and improved cosmetic outcomes. Hence researchers from Osaka National Hospital, Japan conducted a study to assess the practicality and safety of RPS when used for treating full-thickness rectal prolapse.
A retrospective study was carried out to analyze 37 patients who underwent laparoscopic rectopexy for full-thickness rectal prolapse between October 2012 and December 2018. Out of these, 10 patients underwent traditional multiport surgery (MPS), while 27 patients were treated using the reduced port surgery (RPS) technique. Where laparoscopic posterior mesh rectopexy, also known as the Wells procedure, is the standard surgical method for addressing full-thickness rectal prolapse, the authors also conducted an RPS. In RPS, surgeons utilized a multi-channel access device combined with an additional 12-mm right-hand port to complete the procedure. The primary outcome of the study was to evaluate short-term outcomes for both RPS and MPS by examining several metrics, including operative time, blood loss, postoperative complication rates, and the duration of hospital stay after surgery.
Findings:
- Upon comparing the two groups, the results showed no statistically significant differences in median operative times, blood loss volumes, postoperative complication rates, or the length of hospital stays between patients undergoing MPS and those treated with RPS.
- Both techniques appeared to be equally effective and safe in managing full-thickness rectal prolapse.
- However, RPS was found to have significantly smaller wound size suggesting better cosmetic outcomes.
Despite these promising findings for RPS, the study highlights that further research is necessary to establish its superiority over MPS. The retrospective nature of the study and the small sample size limit the ability to draw definitive conclusions. The authors suggest that a prospective, randomized, controlled trial is needed to rigorously assess whether RPS offers any distinct advantages in terms of clinical outcomes, patient recovery, and overall efficacy when compared to traditional multiport approaches. In conclusion, while reduced port laparoscopic posterior mesh rectopexy shows potential as a viable therapeutic option for full-thickness rectal prolapse, the current evidence does not demonstrate significant differences between RPS and MPS in key perioperative outcomes. Future research with a more robust study design is essential to determine if RPS could eventually replace or become preferred over MPS in clinical practice.
Further reading: Kusunoki, C., Uemura, M., Osaki, M. et al. Reduced port laparoscopic rectopexy for full-thickness rectal prolapse. BMC Surg 24, 246 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-024-02545-6
BDS, MDS
Dr.Niharika Harsha B (BDS,MDS) completed her BDS from Govt Dental College, Hyderabad and MDS from Dr.NTR University of health sciences(Now Kaloji Rao University). She has 4 years of private dental practice and worked for 2 years as Consultant Oral Radiologist at a Dental Imaging Centre in Hyderabad. She worked as Research Assistant and scientific writer in the development of Oral Anti cancer screening device with her seniors. She has a deep intriguing wish in writing highly engaging, captivating and informative medical content for a wider audience. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751