- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Topical lidocaine/diltiazem significantly improves pain after Rubber Band Ligation of Hemorrhoids
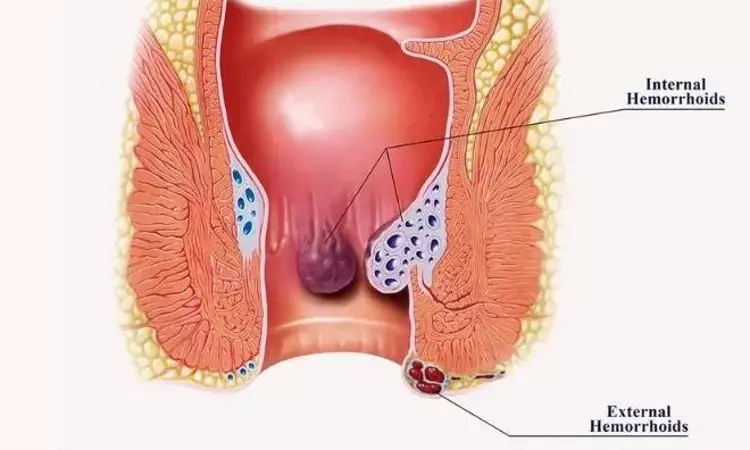
A new study by Allan Kwok and team showed that topical lidocaine enhances analgesia in the short term, while a combination of lidocaine and diltiazem improves analgesia and increases patient satisfaction after hemorrhoid banding. The findings of this study were published in Diseases of the Colon & Rectum.
Rubber band ligation of hemorrhoids produces less pain than excisional hemorrhoidectomy, however many patients still have severe post-procedure discomfort. In order to find out whether topical lidocaine, with or without diltiazem, is more efficient than a placebo for analgesia following hemorrhoid banding, this study was carried out.
This investigation was a prospective, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled experiment. Patients were given a placebo, 2% lidocaine, or 2% lidocaine plus 2% diltiazem. In Australia, this study was carried out at two public teaching hospitals affiliated with universities and two private hospitals. Consecutive hemorrhoid banding patients under the age of 18 were chosen. Topical ointments were used post-procedure three times each day for five days as an intervention. The primary end measures included the visual analogue pain score, the use of opiate analgesics, and patient satisfaction.
The key findings of this study were:
99 suitable patients out of 159 total were randomized (33 in each group).
Comparing the lidocaine and lidocaine/diltiazem groups to the placebo group, the pain ratings were lower at an hour (OR 4.15 [1.12-15.41] p = 0.03) and (OR 3.85 (1.05-14.11) p = 0.04).
Patients in the group that received lidocaine/diltiazem reported higher levels of satisfaction (OR 3.82 [1.28-11.44], p = 0.02) and were also more likely to tell others about the procedure (OR 9.33 [1.07-81.72], p = 0.04).
Compared to the placebo group, patients receiving lidocaine/diltiazem needed around 45% less overall and in-hospital analgesia.
None of the groups' complications varied from one another.
In conclusion, following rubber band ligation of hemorrhoids, topical lidocaine/diltiazem ointment-associated improved analgesia was seen.
Reference:
Kwok, A. M. F., Smith, S. R., Zhao, J., Carroll, R., Leigh, L., & Draganic, B. (2023). Topical Lidocaine or Lidocaine/Diltiazem Ointment Following Rubber Band Ligation of Hemorrhoids: A Prospective Three-Armed Randomized Controlled Trial. In Diseases of the Colon & Rectum: Vol. Publish Ahead of Print. Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health). https://doi.org/10.1097/dcr.0000000000002774
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


