- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy Preserves Kidney Function in Patients with Severe CKD: Study
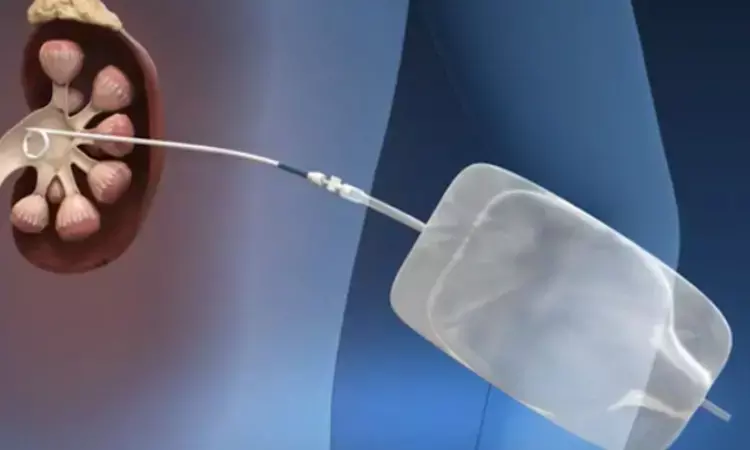
Researchers have determined in a new study that percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL), a common method for the removal of large kidney stones, maintains renal function in those with moderate to severe chronic kidney disease (CKD). The study was published in the World Journal of Urology by Vinay D. and colleagues.
The study evaluated patients with a baseline preoperative estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of less than 45, categorized as CKD stage ≥3b. A total of 29 patients were included in this cohort, with 83% classified specifically as CKD 3b. Preoperative and postoperative eGFR levels were compared to evaluate alterations in renal function. Outcomes examined were progression to dialysis, ∆eGFR (delta change in eGFR), and CKD stage transitions. For comparison purposes, control groups included patients with preoperative stages 3a CKD, 2 CKD, and ≤1 CKD, matched with the CKD ≥3b cohort.
Key Findings
At baseline, the median preoperative eGFR of the CKD ≥3b group was 38 (IQR 31–42). Median renal function follow-up was 8 months (IQR 2–13).
Dialysis-free survival at one year was 87%, which meant that most of the patients managed to stay away from end-stage renal disease.
No difference was noted between preoperative and postoperative eGFR (p=0.97) and median ∆eGFR was 0 (IQR −6 to 6). Out of CKD stage changes, 62% of patients stayed the same, 21% had improvement, and only 17% had worsening.
The ∆eGFR and CKD stage results in the CKD ≥3b group were similar to patients with CKD stages 3a and 2, and superior to those with CKD stage 1 (p=0.02).
In moderate to severe CKD patients, PCNL was concordant with stable or improved renal function in the majority, with a low incidence of deterioration to dialysis. Such findings attest to the efficacy and safety of PCNL in the treatment of large kidney stones in high-risk CKD patients. Specialists can handle such situations with increased assurance, understanding that PCNL does not significantly impair kidney function and frequently is conducive to stability or improvement over the intermediate term.
Reference:
Durbhakula, V., Savin, Z., Frangopoulos, E. et al. Should percutaneous nephrolithotomy be performed in patients with severe chronic kidney disease? A closer look at renal function outcomes. World J Urol 43, 533 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-025-05906-9
Dr Riya Dave has completed dentistry from Gujarat University in 2022. She is a dentist and accomplished medical and scientific writer known for her commitment to bridging the gap between clinical expertise and accessible healthcare information. She has been actively involved in writing blogs related to health and wellness.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


