- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Pre-dialysis hyperkalemia highly prevalent among hemodialysis patients, Finds study
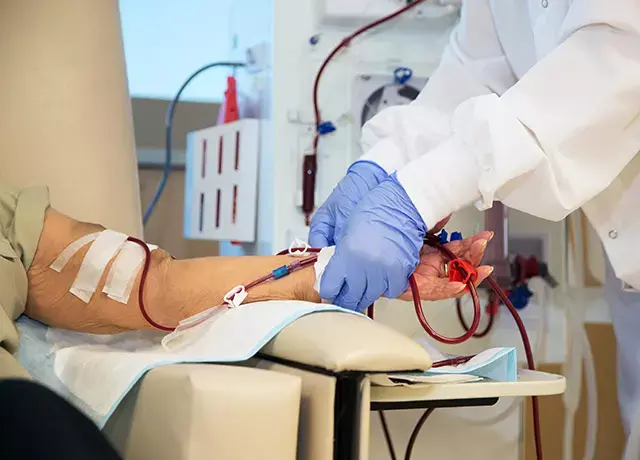
Patients with end-stage renal disease on maintenance dialysis have a high risk of developing hyperkalemia, generally defined as serum potassium (K+) concentrations of >5.0 mmol/l, particularly those undergoing maintenance hemodialysis.
A recent research presented at the National Kidney Foundation Spring Clinical Meetings (virtual meeting) highlighted the fact that there is "relatively high" prevalence rate of pre-dialysis hyperkalemia among patients on hemodialysis, most commonly appreciated in women and younger patients.
Kerry Cooper and colleagues conducted a RE-UTILIZE study wherein the team of researchers included a total of 9,347 participants with at least one potassium lab result present in the retrospective observational cohort study. Of these participants, 58% were men, 49% were older than 66 years and 56% were undergoing hemodialysis.
The occurrence of pre-dialysis HK was analyzed during the course of a year and a sensitivity analysis was used to report the prevalence of hyperkalemia at 1- and 3-month intervals. Furthermore, a logistic regression model was used to examine the prevalence of hyperkalemia and patient characteristic associations.
The researchers found out that any pre-dialysis hyperkalemia (K+ >5 [mEq/L]) had occurred in 38% of patients within 1 month, 52% within 3 months and 74% within 1 year of Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS) enrollment. Also, the characteristic analysis identified women, patients aged 80 years or younger and Hispanic individuals as having a higher annual HK prevalence.
Hence, the authors concluded that using Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study survey data, the RE-UTILIZE study sheds lights on the low levels of prescribed potassium binder in contrast with the high levels of recurrent HK in those receiving long-term dialysis.
This data can help support new strategies for clinicians to address pre-dialysis HK more effectively by considering the use of novel potassium binders on non-dialysis days, they further added.
The authors also inferred that further clinical research on annual hyperkalemia prevalence in patients on hemodialysis is needed to inform clinical practice and improve patient care.
For further reference, log into:
Agiro A, et al. Abstract #237. Presented at: National Kidney Foundation Spring Clinical Meetings (virtual meeting); April 6-10, 2021.
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


