- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Urethroplasty effective way to manage pelvic fracture urethral distraction defect in preschool boys: Study
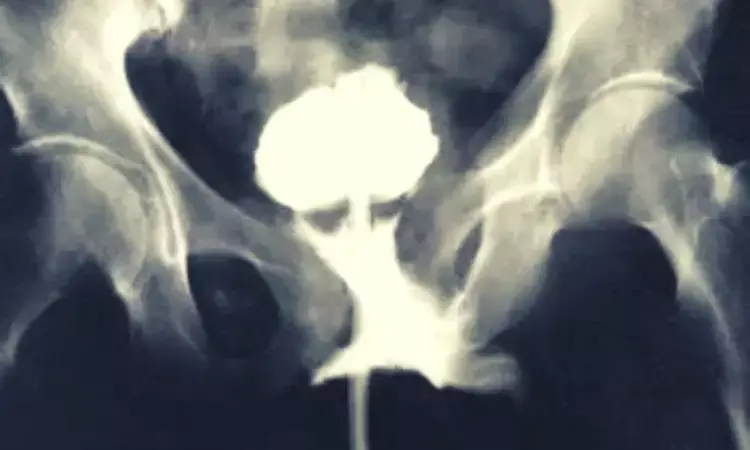
China: A recent study in the journal Urology has preliminary confirmed that progressive anastomotic urethroplasty strategy can ensure a high success rate in preschool boys with pelvic fracture urethral distraction defect (PFUDD). PFUDD in young boys is a uncommon but challenging problem for both the urologist and parent.
In the study, Yinglong Sa, Shanghai Eastern Institute of Urologic Reconstruction, Shanghai, China, and colleagues shared the cases of pelvic fracture urethral distraction defect in preschool boys and evaluated the transperineal anastomotic urethroplasty strategy for the treatment.
For this purpose, the researchers retrospectively reviewed 8 preschool boys (<6 years) with PFUDD underwent the transperineal anastomotic urethroplasty between January 2010 and May 2021. Etiology was traumatic pelvic fracture in all boys.
The type of trauma was fall injury in 1 and vehicle crush injury in 7. Urethroplasty was performed at least 3 months after initial trauma or the last failed intervention. One of them had PFUDD associated with urethrorectal fistula, he received urethroplasty combined with fistula repair. Urethroplasty was considered successful when the patency and continuity of urethra was restored and there was no requirement of further interventions.
Following were the study's key findings:
· Follow-up was obtained in all the 8 preschool boys for 3-135 (median: 65) months. The average age was 4.1 years old.
· Of the 8 boys, 1 developed urinary incontinence, only occurring after high-intensity exercise such as running.
· Potency state could not be evaluated for all boys due to the young age.
· One boy reported having normal morning erection after a follow-up of 135 months.
"PFUDD in preschool boys is a challenge for both the urologist and parent," wrote the authors. "Our study preliminarily confirmed that the progressive anastomotic urethroplasty strategy can ensure a high success rate."
Reference:
The study titled, "Pelvic Fracture Urethral Distraction Defects in Preschool Boys: How to Recognize and Manage?," was published in the journal Urology.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


