- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Chinese Herbal Formula Equals Losartan For Treatment of Mild Hypertension
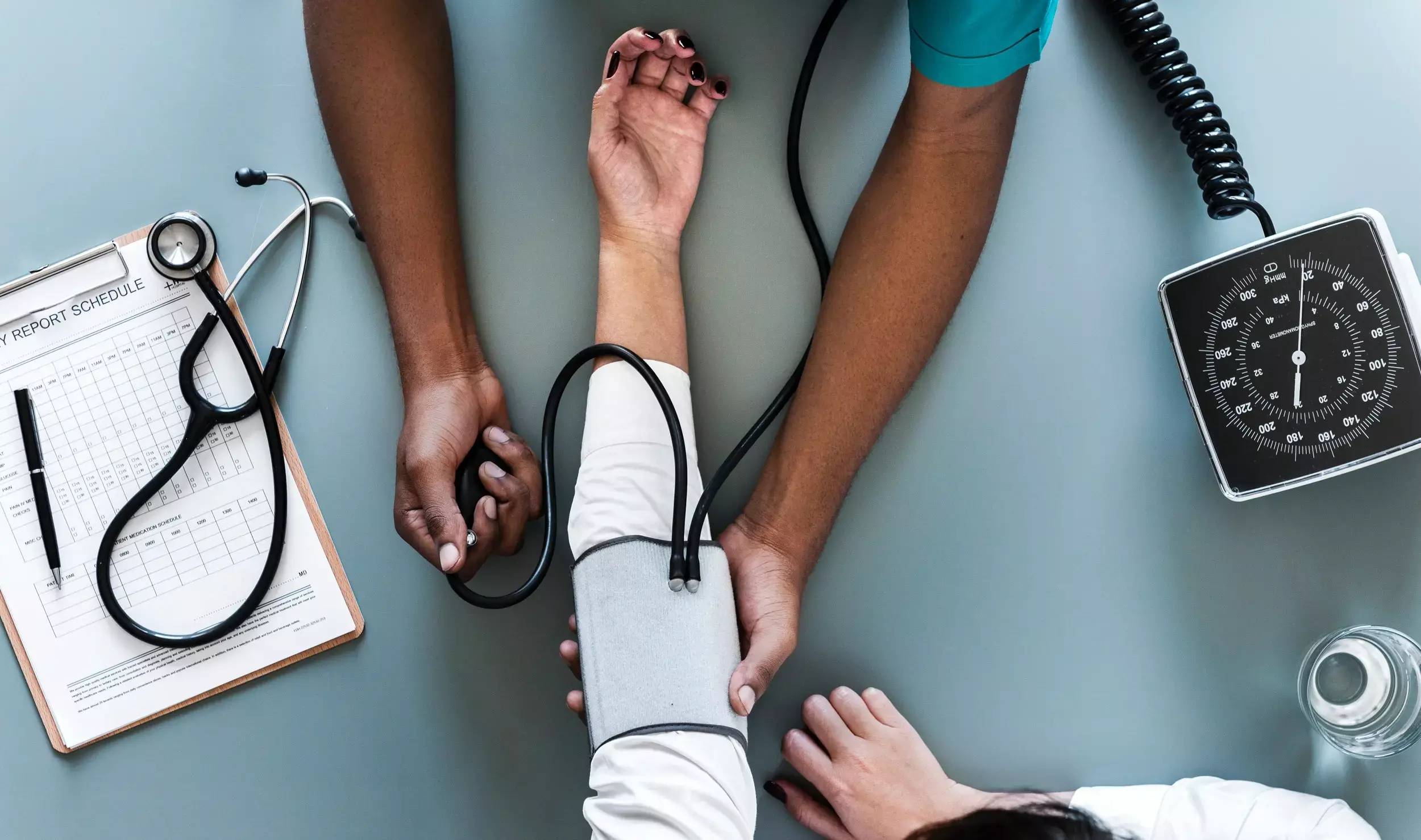
Hypertension is one of the most challenging public health problems worldwide. A recent study suggests that Songling Xuemaikang capsule (SXC)—a Chinese herbal formula is as effective as losartan in reducing Blood Pressure (BP) among patients with mild hypertension. The study findings were published in the journal Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes on February 02, 2022.
Previous studies demonstrated that the Songling Xuemaikang capsule (SXC) was effective for essential hypertension. However, the efficacy of SXC monotherapy for hypertension remains unclear. Therefore, Dr Ying Gao and her team conducted a study to compare the blood pressure (BP)–lowering efficacy and safety of SXC versus losartan in patients with essential hypertension.
The researchers conducted a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, noninferiority in which 628 patients with mild essential hypertension were randomly assigned to receive either SXC (n=314) or losartan (n=314) for 8 weeks. The major outcome assessed was the change in sitting diastolic BP from baseline to 8 weeks, with a predefined noninferiority margin of −2.5 mm Hg.
Key findings of the study:
- In a primary analysis based on the intention-to-treat principle, the researchers found that the change in diastolic BP from baseline to 8 weeks was similar between the SXC and losartan groups (−7.9 [8.0] versus −8.1 [7.9]).
- They observed that the lower boundary of 95% CI was above the margin of −2.5 mm Hg, showing noninferiority.
- They noted that the results were consistent with per-protocol analysis.
- They observed that the SXC produced greater improvements in total hypertension symptom score (−5.7 [4.2] versus −5.0 [4.0]) and total cholesterol (−0.1 [1.0] versus 0.1 [1.2]).
- They found no differences between groups in the other BP and patient-reported outcomes.
- They noted that the incidence and severity of adverse events were similar between groups.
The authors concluded, "SXC was well tolerated and demonstrated non-inferior to losartan in BP lowering in patients with mild hypertension. SXC might be an alternative for mild hypertension, particularly for patients with a preference for natural medicine."
For further information:
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


