- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Short-term dual antiplatelet therapy effective after carotid artery stenting, claims research
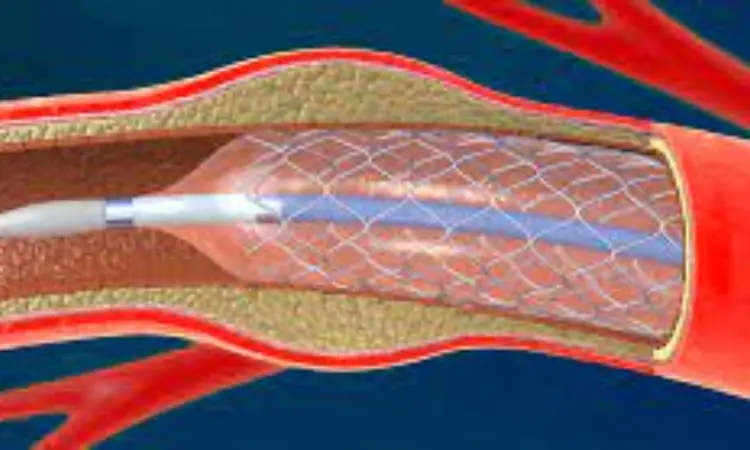
A recent study published in the Stroke; a Journal of Cerebral Circulation found that short-duration dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) is as effective and safe as long-duration DAPT for patients undergoing carotid artery stenting (CAS). The findings could help clinicians to optimize post-procedure treatment for patients at risk of complications from extended DAPT use.
Carotid artery stenting (CAS) is a less invasive alternative to carotid endarterectomy for patients with carotid artery stenosis which significantly increases the risk of ischemic stroke. After CAS, DAPT (combination of aspirin and clopidogrel) is prescribed to prevent clot formation and subsequent strokes. This study was set out to determine whether a shorter duration of DAPT could provide comparable protection while minimizing risks of bleeding or other adverse effects.
This research utilized data from the Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service from 2007 to 2019 and analyzed outcomes for 12,034 patients who underwent CAS. This study divided patients into 2 groups based on the duration of DAPT where the patients who received DAPT for at least 90 days but less than six months were included in the Short-DAPT, while the Long-DAPT group comprised patients who maintained DAPT for longer than six months.
The primary outcome assessed was a composite of ischemic stroke, gastrointestinal bleeding, and intracranial hemorrhage within 12 months after transitioning to single antiplatelet therapy. Among the 12,034 patients studied, 2,529 were in the short-DAPT group, while 9,505 were in the long-DAPT group.
In the short-DAPT group, 41 patients (1.6%) experienced ischemic stroke, 22 patients (0.9%) had gastrointestinal bleeding, and 4 patients (0.2%) suffered intracranial hemorrhage. In the long-DAPT group, 108 patients (1.1%) had ischemic stroke, 87 patients (0.9%) experienced gastrointestinal bleeding, and 4 patients (0.04%) suffered intracranial hemorrhage.
The overall rate of the composite primary outcome was similar between the groups (2.5% for short-DAPT versus 2.1% for long-DAPT), with no statistically significant difference (adjusted hazard ratio 0.869; P=0.337). Overall, the study suggests that short-duration DAPT is a viable option after CAS by providing comparable clinical outcomes to long-duration DAPT in terms of stroke prevention and bleeding complications.
Reference:
Yoo, J., Lim, H., & Seo, K.-D. (2025). Optimal duration of dual antiplatelet therapy after carotid artery stenting: A nationwide cohort study. Stroke; a Journal of Cerebral Circulation. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.124.048743
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


