- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Study Finds Elevated Uric Acid Predicts High-Risk Plaques on Coronary CT Angiography
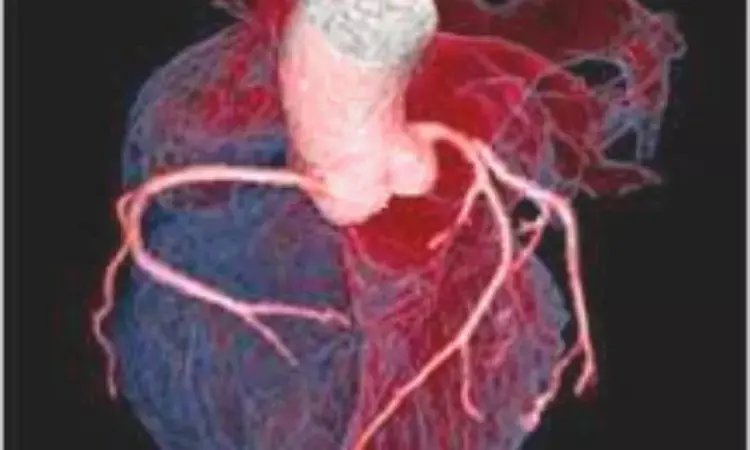
China: A recent study has found that elevated serum uric acid (UA) levels are independently associated with the presence of high-risk coronary artery plaques, suggesting that measuring UA could improve cardiovascular risk assessment.
- Higher serum uric acid (UA) levels were significantly associated with increased risk of high-risk plaques (HRPs) after adjusting for age, sex, type 2 diabetes, smoking, obstructive coronary artery disease, total plaque volume, and other plaque characteristics.
- Each standard deviation increase in serum UA nearly tripled the odds of having an HRP (OR 2.96).
- Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis showed strong predictive ability of UA for HRPs, with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.86.
- Subgroup analyses based on sex, diabetes, smoking, alcohol use, and Agatston score demonstrated consistent associations, with no significant effect modification.
Reference:
Long X, Jing Y, Haitao Z. Association between serum uric acid and high-risk plaques assessed by coronary CT angiography. Open Heart. 2025;12:e003579. https://doi.org/10.1136/openhrt-2025-003579
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


