- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Unusual Case of Odontogenic Keratocyst with Atypical and Aggressive Behavior
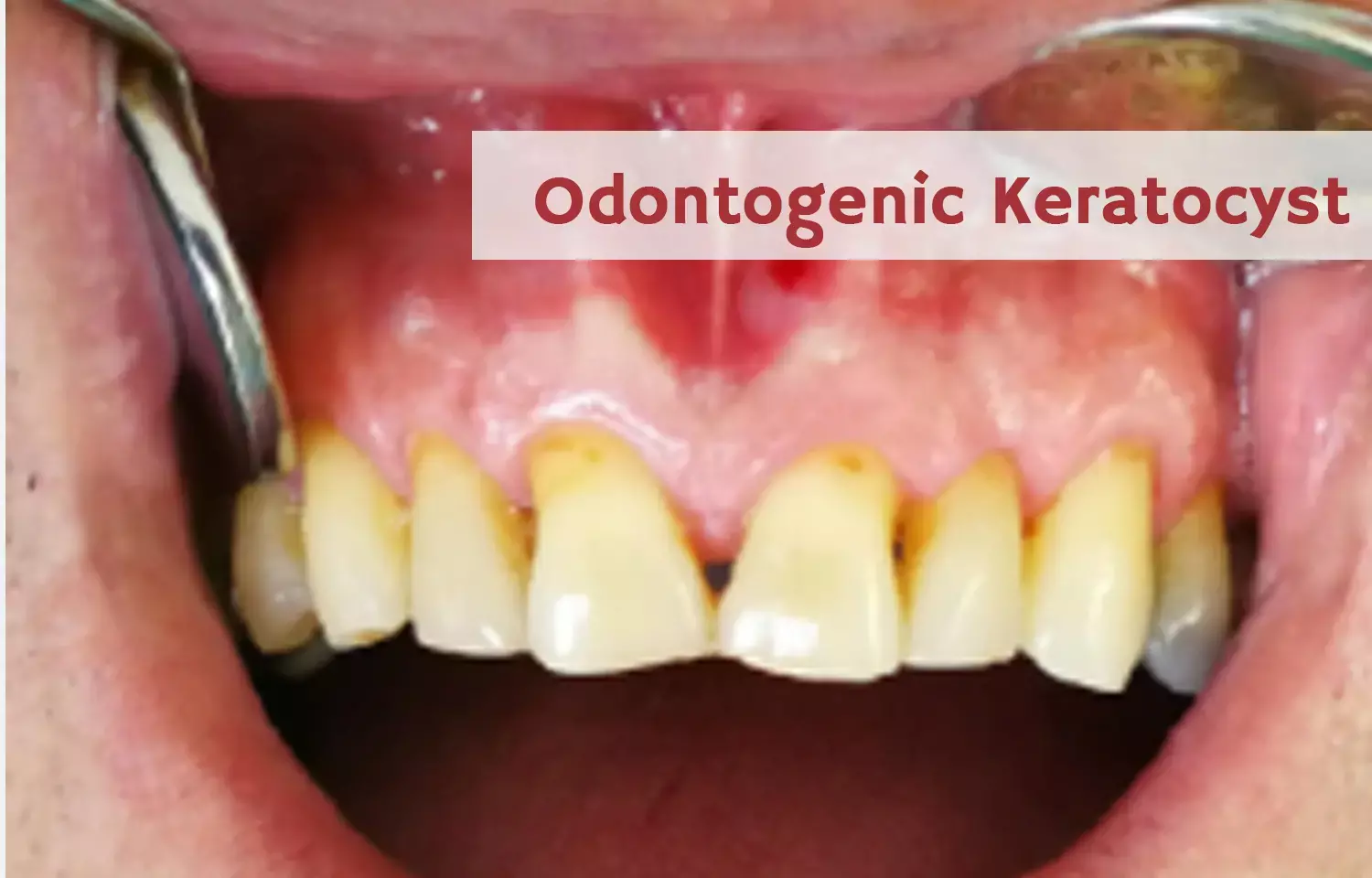
Rafael Martins Afonso Pereira and colleagues from the School of Dentistry, University Center of Patos de Minas (UNIPAM), Patos de Minas, Minas Gerais, Brazil recently obserevd that odontogenic keratocyst can present atypical behavior and characteristics.
The study is published in the Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Journal.
The Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC) is a potentially destructive cyst with a high probability of recurrence. This pathological lesion represents about 11% of all odontogenic cysts, being considered the third most common cyst of the jaws and with a slight predilection for the male gender. Clinically, patients affected by OKC are generally asymptomatic and 80% of them remain in this form for about 2 years.
The authors studied the case of a 14 years old female patient who presented with painful symptoms and asymmetry on the left side of the face. After performing imaging tests, it was possible to observe an extensive radiolucent lesion with cortical bone expansion associated with tooth 17, displaced by the lesion. Due to the patient's clinical and imaging characteristics, the initial diagnostic hypothesis was a dentigerous cyst.
However, At the beginning of the surgical procedure, before the initial incision, an aspiration puncture was performed, which resulted in a dense, whitish-colored liquid compatible with keratin. Thereafter the incision and curettage, the presence of a thin, friable fibrous capsule and cystic lumen containing white solid material compatible with keratin was observed. Thus, a new diagnostic hypothesis of odontogenic keratocyst was established.
The lesion was enucleated and a diagnosis of OKC was determined after histopathological evaluation. The treatment of choice was the complete enucleation of the cyst. The OKC has a high rate of recurrence and, so, it is necessary to know the various risk factors that can influence the reappearance of the injury.
The authors revealed that the method of treating OKC is a controversial subject that generates much discussion.
Therefore, they concluded that "the present case demonstrated that the odontogenic keratocyst can present atypical behavior and characteristics, with the presence of bone cortical expansion, displacement of teeth, facial asymmetry and painful symptoms."
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


