- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
A new approach makes it easier for AI to spot pulp cavities: Study
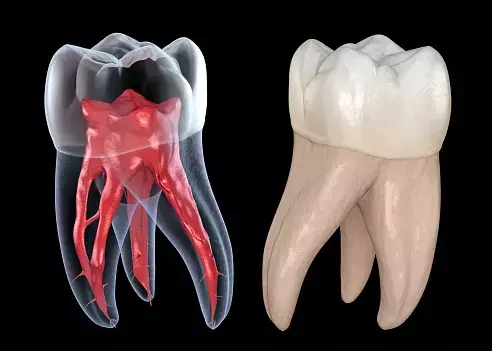
Combining cone-beam CT (CBCT) and micro-CT images as training data can help artificial intelligence (AI) models identify the location of teeth and pulp cavities in CBCT images, according to a recent study published in the Journal of Endodontics.
A group of researchers from China proposed a novel data pipeline based on micro-CT data for training the U-Net network to realize the automatic and accurate segmentation of pulp cavity and tooth on cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images.
The researchers collected CBCT data and micro-CT data of thirty teeth. CBCT data were processed and transformed into a small field of view and high-resolution CBCT images of each tooth. Twenty-five sets were randomly assigned to the training set and the remaining five sets to the test set. We used two data pipelines for U-Net network training: one manually labelled by an endodontic specialist as the control group, and one processed from the micro-CT data as the experimental group. The 3D models constructed using micro-CT data in the test set were taken as the ground truth. Dice similarity coefficient (DSC), precision rate (PR), recall rate (RR), average symmetric surface distance (ASSD), Hausdorff distance (HD) and morphological analysis were utilized for performance evaluation.
The results of the study are as follows:
· The segmentation accuracy of the experimental group measured by DSC, PR, RR, ASSD, and HD were 96.20±0.58%, 97.31±0.38%, 95.11±0.97%, 0.09±0.01mm, and 1.54±0.51mm in tooth and 86.75±2.42%, 84.45±7.77%, 89.94±4.56%, 0.08±0.02mm, 1.99±0.67mm in the pulp cavity, respectively, which were better than the control group.
· Morphological analysis suggested the segmentation results of the experimental group were better than those of the control group.
Thus, the researchers concluded that this study proposed an automatic and accurate approach for tooth and pulp cavity segmentation on CBCT images, which can be applied in researches and clinical tasks.
Reference:
Micro-Computed Tomography Guided Artificial Intelligence for Pulp Cavity and Tooth Segmentation on Cone-beam Computed Tomography by Lin X et. al published in the Journal of Endodontics.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2021.09.001
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


