- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Clotrimazole as adjunct to endodontic irrigation protocol improves pulpectomy results
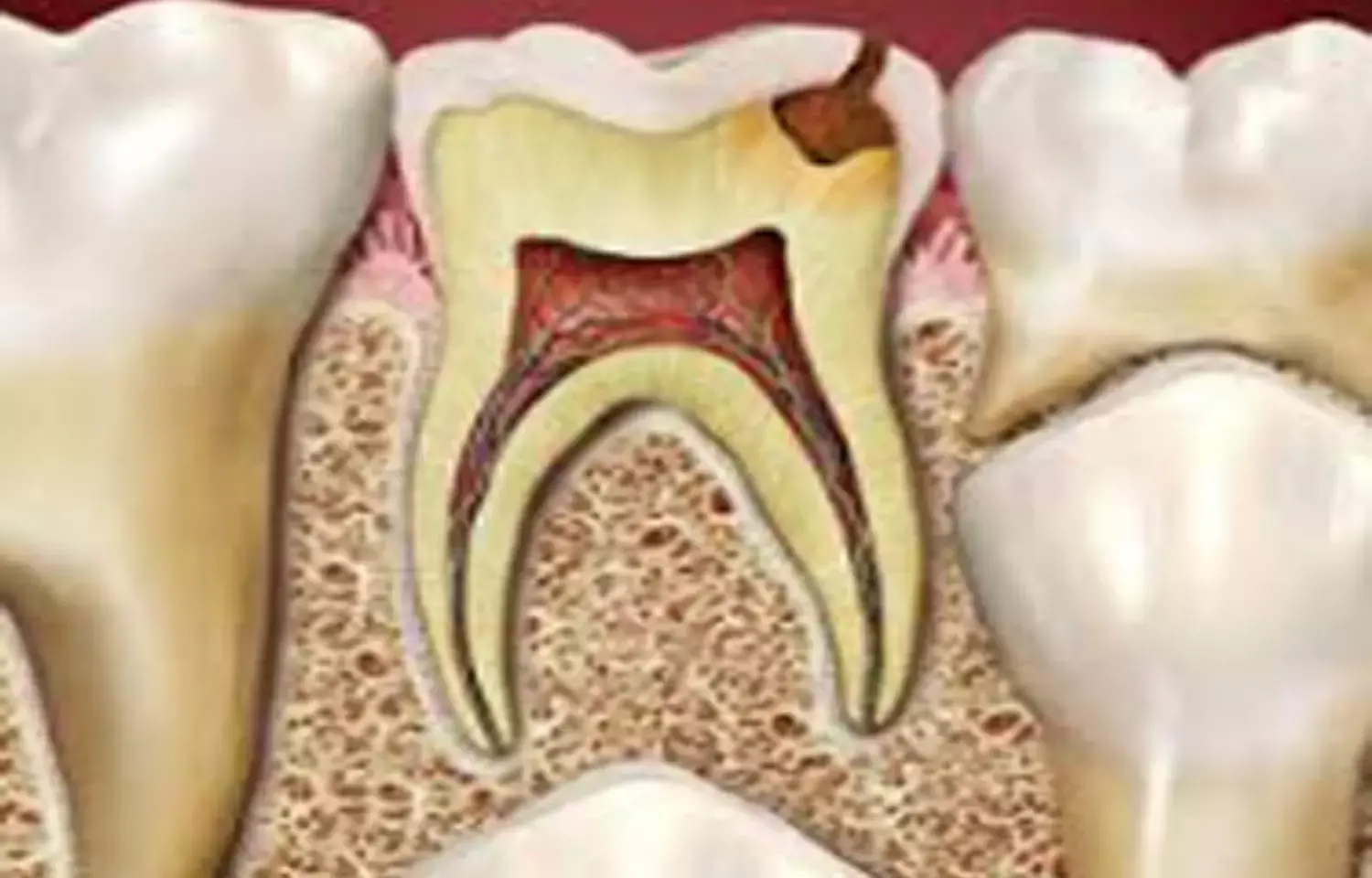
According to recent research, it is found that one percent Clotrimazole (antifungal) can be utilized as an adjunct in the endodontic irrigation protocol for better success of pulpectomy in children.
The study is published in the Journal of Indian Society of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry.
Several factors are involved in the development of pulp and periapical disease in primary and permanent teeth, with dental caries being the main factor. Although these factors are similar, the clinical management of a primary or permanent tooth with pulp or periapical disease may be quite different. Despite endodontic infections being a common problem in the primary dentition, some of the infected primary teeth can remain functional until the exfoliation through endodontic treatment. The primary endodontic treatment goal must be to optimize root canal disinfection and to prevent reinfection.
Therefore, Pallavi Anand and colleagues from the Department of Pediatric and Preventive Dentistry, ITS-CDSR, Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh, India conducted the present study to compare the antifungal efficacy of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy, LASER, and 1% clotrimazole as irrigants by reducing the colony-forming units (CFU) of Candida albicans in the infected root canals of primary teeth.
The authors performed pulp therapy on deciduous mandibular second molars of 20 healthy children aged 5–8 years. The children were divided into four groups of intracanal disinfection protocols: Group 1 (n = 5) – Sodium Hypochlorite, Group 2 (n = 5) – Photodynamic, Group 3 (n = 5) – Normal saline with LASER, and Group 4 – (n = 5) Antifungal. Disinfection potential was compared by collecting samples one just after access opening and the other after the experimental groups using paper points. The samples were cultured and incubated for 48 h to check the change in CFU of the fungi.
The key finding noted in the study was that there was no significant difference found between the different groups. However, complete inhibition of C. Albicans CFU was seen with Group 4.
Hence, Anand concluded that "One percent Clotrimazole (antifungal) can be utilized as an adjunct in the endodontic irrigation protocol for better success of pulpectomy in children."
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


