- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Ridge preservation may reduce ridge resorption in sockets of periodontally compromised teeth
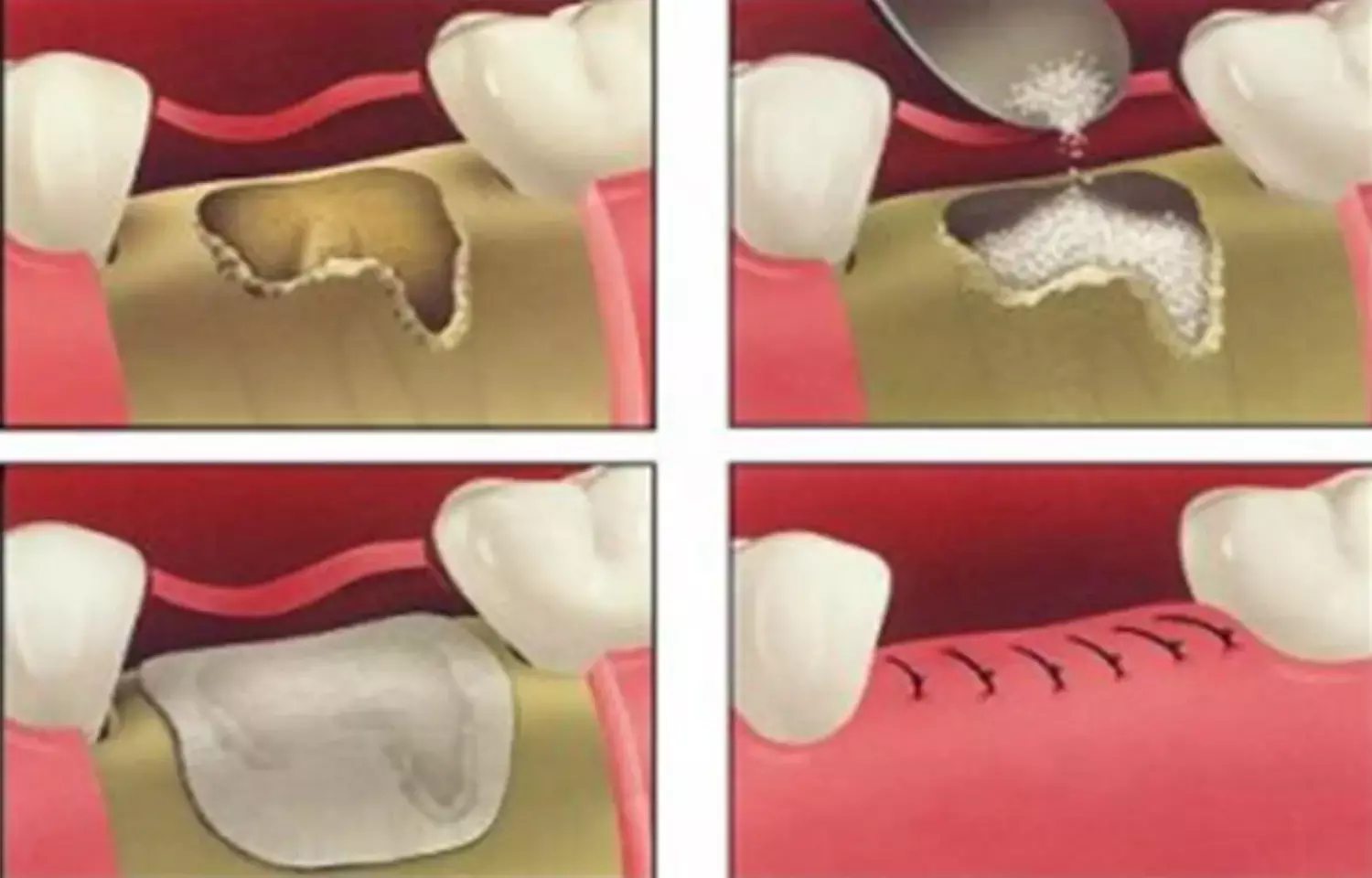
Researchers have recently observed that ridge preservation in extraction sockets of periodontally compromised teeth was effective in reducing the amount of ridge resorption.
The study is published in the Journal of Clinical Periodontology.
The resorption of bone following extraction may present a significant problem in implant and restorative dentistry. Ridge preservation is a technique whereby the amount of bone loss is limited.
Hence, Heithem Ben Amara and colleagues from the Department of Periodontology and Dental Research Institute, Translational Research Laboratory for Tissue Engineering (TTE), School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea conducted this study to verify whether ridge preservation is effective in the reduction of dimensional loss and in bone formation compared to spontaneous healing in extraction sockets of periodontally compromised teeth.
The authors studied a total of twenty‐six subjects requiring tooth extraction for stage III/IV periodontiti all of whom were randomly assigned to one of two interventions: alveolar ridge preservation using collagenated bovine bone mineral and a resorbable collagen membrane (test, RP) or spontaneous healing (control, SH).
Six months later, postoperative cone‐beam computed tomography (CBCT) was performed to measure the linear and volumetric changes of the sockets compared to baseline scans. Biopsies were retrieved at the implant site for histomorphometric calculations. Nonparametric tests were applied for statistical analysis.
The following findings were highlighted-
a. Significantly less shrinkage occurred in RP compared to SH, mainly in the crestal zone.
b. The width loss difference between groups was 3.3 mm and 2.2 mm at 1 mm and 3 mm below the crest, respectively (p<0.05).
c. RP yielded a gain in socket height of 0.25 mm, whereas a loss of ‐0.39 mm was observed in SH (p<0.05).
d. The percentage of volume loss recorded in RP was also less than that recorded in SH (‐26.53% vs ‐50.34, p<0.05).
e. Significantly less bone proportion was detected in biopsies from RP (30.1%) compared with SH (53.9%).
f. A positive association between baseline bone loss and ridge shrinkage was found in SH but not in RP.
Therefore, the researchers concluded that "ridge preservation in extraction sockets of periodontally compromised teeth was effective in reducing the amount of ridge resorption."
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


