- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Study finds IBD patients highly susceptible to severe periodontitis
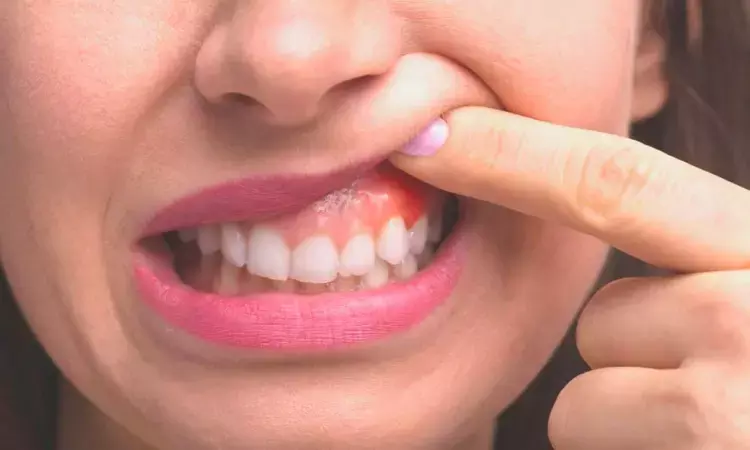
A new study by Kristina Bertl and team found that patients with ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD) had considerably higher probabilities of having severe periodontitis, a condition that causes greater tooth loss in the former and lower self-perceived oral health in the latter. The findings of this study were published in the Journal of Clinical Periodontology.
In many ways, the aetiopathogenesis of periodontitis and inflammatory bowel disorders are comparable. Both disorders entail an overly inflammatory reaction in the intestinal or oral mucosa in a vulnerable host in response to a microbial stimulus. As a first-line defense mechanism, neutrophils infiltrate large amounts of tissue during this reaction, causing tissue damage in the process. This questionnaire-based case-control study sought to determine if patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease self-reported oral health and periodontitis differently from matched controls without inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
An online survey was given that asked about general anamnestic details, the diagnosis of IBD, and dental health. As outcome criteria, tooth loss, severe periodontitis, and self-perceived overall dental and gum health were listed.
The key findings of this study were:
1. Analysis was based on responses from 3429 control subjects and 1108 IBD patients.
2. In comparison to controls, patients with IBD reported considerably lower oral health and more periodontal issues.
3. Regression analyses adjusted for relevant confounders revealed significantly higher odds for patients with UC and CD compared to controls for fair or poor self-perceived overall dental and gum health and for severe periodontitis; patients with CD also showed 91% higher odds for having fewer than 20 remaining teeth.
The current findings are consistent with the idea that UC and CD patients have much higher probabilities of having severe periodontitis, as well as fair or poor self-perceived overall dental and gum health. CD patients also appear to be more seriously impacted and to experience greater tooth loss. Therefore, it is highly advised that IBD patients be kept under careful observation in order to stop the development of periodontitis and/or slow down its progression and tooth loss.
Reference:
Bertl, K., Burisch, J., Pandis, N., Bruckmann, C., Klinge, B., & Stavropoulos, A. (2022). Periodontitis prevalence in patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease ‐ PPCC: A case–control study. In Journal of Clinical Periodontology (Vol. 49, Issue 12, pp. 1262–1274). Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.13615
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


